How Mule DevKit Works
Mule DevKit uses annotations to generate Mule integration code, XML schemas, and Studio interfaces, so writing Mule extensions is as simple as writing, and annotating, a Java class. Mule DevKit handles the details so you can focus on the core of the module rather than how it interacts with Mule.
Annotation Processor
When Java source code is compiled, compiler plug-ins called annotation processors process the annotations. Annotation processors can produce informational messages or create additional Java source files or resources which they may, in turn, compile and process. They can also modify the annotated code.
At heart, Mule DevKit is an annotation processor your POJO’s annotations and generates code accordingly. There are several ways to execute an annotation processor:
-
you can use the standalone tool app
-
you can use a Maven plugin
-
you can use your Java IDE, most of which support annotation processors
Mule DevKit uses annotations that mimic Mule vocabulary making it easy for developers to understand the annotation processor’s actions. For example, in response to some annotations, Mule DevKit creates message processors that you can use directly in Mule Studio.
High Level Overview
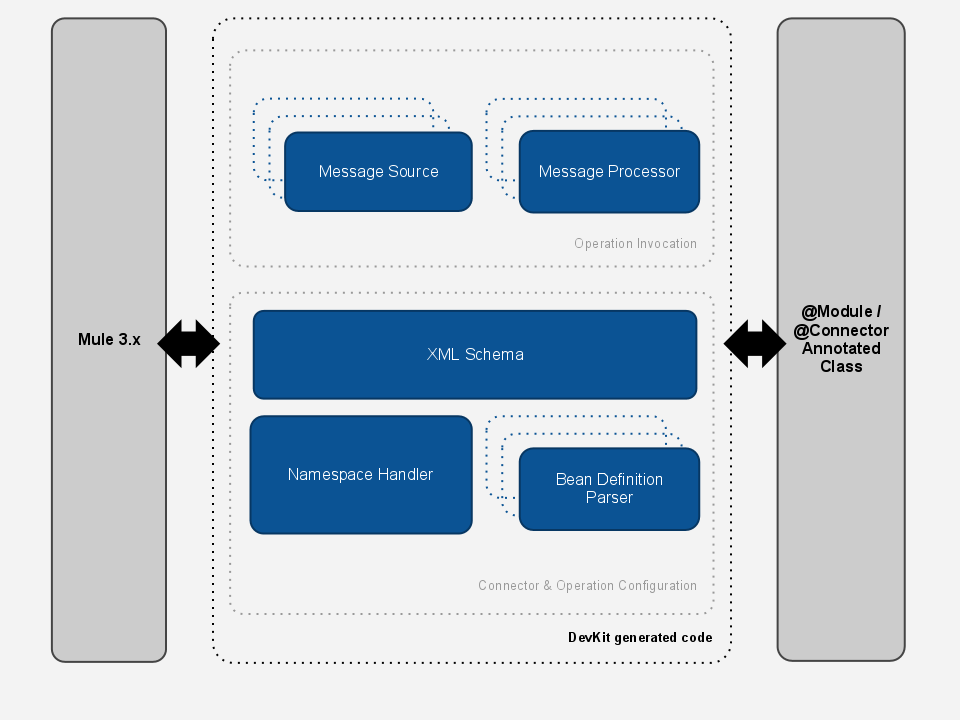
The DevKit relies on the schema-based extension mechanism of the Spring framework. Mule DevKit’s Annotation Processing Tool generates Java code that acts as a bridge between annotated POJOs and Mule (see image below).

The types of classes the annotation processor generates depends on the annotations.



