
Creating a Connector Using a Java Client Library
| DevKit is compatible only with Studio 6 and Mule 3. To build Mule 4 connectors, see the Mule SDK documentation. |
This example walks you through the implementation of an Anypoint Connector for an API exposed through a Java client library. Follow the process outlined in this document to build a Java client library-based connector for any service.
Java client libraries are in many cases the best option for integrating with a remote service. If the client library is officially supported by the application provider, or even if it is unofficial but widely used, it likely implements best practices for integrating with the application in common use cases.

Assumptions
This document assumes familiarity with the Anypoint connector architecture as described in Anypoint Connector Concepts. Furthermore, it assumes that you have created a new connector project as described in Creating an Anypoint Connector Project.
Client Library-Based Connector Architecture
The overall architecture of a client library-based connector looks like the image below.
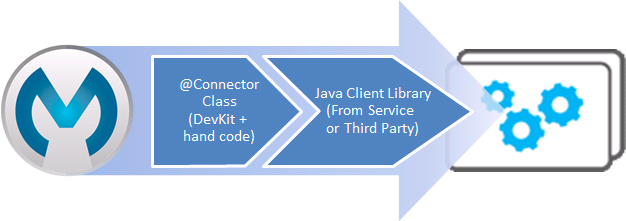
The components of the connector include:
-
The Java client library that exposes the authentication methods and the supported operations
-
Supporting data model entity classes, which typically are defined by the Java client library
-
The
@Connectorclass that you implement based on the skeleton generated by Anypoint DevKit
In practice, although the Java client library usually communicates with a RESTful or SOAP-based Web service, it encapsulates all the required client logic in Java, and sidesteps the added work and complexity of building the client layer of the connector. The client library may also hide non-standard behavior of badly designed Web services behind a more manageable Java façade.
The Example Connector
The example for this discussion is the MuleSoft Twitter connector, which is based on the unofficial but widely used twitter4j client library. The source code for the Twitter Connector on GitHub is available and referenced in the discussions.
|
The Twitter connector illustrates many aspects of DevKit functionality added in the 3.5 releases of Mule, including DataSense Query Language support, OAuth 2 authentication, and paging results from operations. The focus in this discussion will be on the relationship between the client library and the For authentication, the Twitter connector implements an interesting hybrid, defined in TwitterConnector.java:
|
Adding the Client Library to the Connector Project
Depending upon how your client library is delivered, you can add it to your project in one of several ways. For example:
-
If the library is available via Maven, you can add it to your project POM file. For example, Twitter4J can be added as a Maven dependency from the central Maven repository as follows:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.twitter4j</groupId>
<artifactId>twitter4j-core</artifactId>
<version>3.0</version>
</dependency>-
You can simply download the JAR file and add it to the build path in Eclipse or IntelliJ.
-
If the source code is available, you can simply incorporate it into your project.
|
In the case of the Mule Twitter connector, in the current version the source code for Twitter4J is actually included in the connector directly. The Mule connector version of the Twitter4J library has been altered slightly, and the Mule connector accesses some internal classes, and customizes at least one: For unofficial or unsupported client libraries, or any open source client library, this approach has the advantage that you have direct control of the contents of the client library, which you can tailor to work with Mule or to otherwise better fit your use case. (Of course, the tradeoff is that you then have to maintain the library going forward.) |
Defining the @Connector Class
The first step is building the @Connector class basic functionality around connection management and authentication, as indicated in the following sections.
Defining Entity Classes and Exceptions
In general, it is recommended that you define at least two exceptions for your connector: one to indicate connection and authentication-related failures, and another to indicate all other failures – including, for example, an exception for invalid arguments passed to an operation. A separate exceptions package is a good place to define these.
| In the case of the Twitter connector, the exceptions defined by Twitter4J are simply passed directly to Mule. |
Implementing Authentication and Connection Management
Authentication is implemented both in the @Connector class and in the client library. Details of implementing authentication in the @Connector class will depend upon the chosen authentication scheme, and on the client library support for authentication.
For OAuth, the @Connector class OAuth-related functionality may be used to collect required keys and secrets, or this may be managed by the client library by some other means.
For non-OAuth authentication, add @Configurable properties on the @Connector class as described in Defining Configurable Connector Attributes, and take advantage of the connection management framework as described in Implementing Authentication and Connection Management.
The API for the client library will expose methods or method parameters by which you pass those details to the library, either at initialization time or when calling operations. Details will vary by client library.
For details on the different schemes available and DevKit support for them, see:
-
Implementing Authentication and Connection Management for an overview
-
Implementing Connection Management for non-OAuth authentication schemes
-
Implementing OAuth 1.0 Authentication and Implementing OAuth 2.0 Authentication for OAuth-enabled schemes.
Leveraging Twitter4J OAuth Support
The Twitter connector implements an interesting hybrid, defined in TwitterConnector.java:
-
The Twitter4J client library implements its own OAuth support, which the Mule connector leverages
-
Because the connector does not use DevKit’s OAuth support, it is possible to use DevKit’s connection management framework
Thus, we have the class definition with no @OAuth annotation:
@Connector(name = "twitter", schemaVersion = "2.4", description = "Twitter Integration", friendlyName = "Twitter",
minMuleVersion = "3.5", connectivityTesting = ConnectivityTesting.DISABLED)
public class TwitterConnector implements MuleContextAware {...And a @Connect method with a @ConnectionKey set to the OAuth accessKey, and the usual associated @Disconnect, @ValidateConnection and @ConnectionIdentifier methods.
@Connect
public void connect(@ConnectionKey String accessKey, String accessSecret) throws ConnectionException{
ConfigurationBuilder cb = new ConfigurationBuilder();
cb.setUseSSL(useSSL);
cb.setHttpProxyHost(proxyHost);
cb.setHttpProxyPort(proxyPort);
cb.setHttpProxyUser(proxyUsername);
cb.setHttpProxyPassword(proxyPassword);
HttpClientHiddenConstructionArgument.setUseMule(true);
twitter = new TwitterFactory(cb.build()).getInstance();
twitter.setOAuthConsumer(consumerKey, consumerSecret);
if (accessKey != null) {
twitter.setOAuthAccessToken(new AccessToken(accessKey, accessSecret));
setAccessToken(accessKey);
setAccessTokenSecret(accessSecret);
}
}
...
@Disconnect
public void disconnect() {
twitter = null;
}
@ValidateConnection
public boolean validateConnection() {
return twitter != null;
}
@ConnectionIdentifier
public String getConnectionIdentifier() {
return getAccessToken() + "-" + getAccessTokenSecret();
}On the other hand, we have a series of @Processor methods that implement OAuth-related functionality, like getting and managing an access token by calling functions exposed by class twitter4j.Twitter :
/**
* Set the OAuth verifier after it has been retrieved via requestAuthorization.
* The resulting access tokens will be logged to the INFO level so the user can
* reuse them as part of the configuration in the future if desired.
* <p/>
* {@sample.xml ../../../doc/twitter-connector.xml.sample twitter:setOauthVerifier}
*
*
* @param requestToken request token from Twitter
* @param oauthVerifier The OAuth verifier code from Twitter.
* @return Twitter AccessToken info.
* @throws TwitterException when Twitter service or network is unavailable
*/
@Processor
public AccessToken setOauthVerifier(@Optional RequestToken requestToken, String oauthVerifier) throws TwitterException {
AccessToken accessToken;
if (requestToken != null) {
accessToken = twitter.getOAuthAccessToken(requestToken, oauthVerifier);
}
else {
accessToken = twitter.getOAuthAccessToken(oauthVerifier);
}
logger.info("Got OAuth access tokens. Access token:" + accessToken.getToken()
+ " Access token secret:" + accessToken.getTokenSecret());
return accessToken;
}
/**
* Start the OAuth request authorization process.
*/
@Processor
public RequestToken requestAuthorization(@Optional String callbackUrl) throws TwitterException {
RequestToken token = twitter.getOAuthRequestToken(callbackUrl);
return token;
}
...
public String getAccessToken() {
return accessToken;
}
public void setAccessToken(String accessToken) {
this.accessToken = accessToken;
}
public String getAccessTokenSecret() {
return accessTokenSecret;
}
public void setAccessTokenSecret(String accessTokenSecret) {
this.accessTokenSecret = accessTokenSecret;
}And the @Processor methods that actually call Twitter operations do not use the @OAuthProtected annotation:
@Processor
public User showUser() throws TwitterException {
return twitter.showUser(twitter.getId());
}You can dig into this code and use a similar implementation pattern if you are working with a client library that provides its own OAuth support.
Adding an Operation to the @Connector Class
At this point you can start adding operations to the connector.
With a client library, the steps to add an operation include:
-
importing any Java entity classes, defined by the client library, that are used as parameters or return value by the operation, as well as any exceptions the client library may raise
-
adding a
@Processormethod on the@Connectorclass, that calls an operation on the client instance
Depending on your specific client class, you may need to add authentication functionality in the operation methods to handle authentication.
|
Apply a Test-Driven Approach Based on MuleSoft experience, most successful connector implementation projects follow a cycle similar to test-driven development when building out operations on a connector:
Iterate until you cover all the scenarios covered in your requirements for a given operation. Then use the same cycle to implement each operation, until your connector functionality is complete. If your client library is well-documented, the expected behaviors for operations should be clear, and you may be able to get away with less unit testing for edge cases and certain exceptional situations – but bear in mind that your connector is only as reliable as the Java client you based it on. You may ask, "When do I try my connector in Studio?" It is useful, as well as gratifying, to manually test each operation as you go, in addition to the automated JUnit tests. Testing each operation allows you to
Manual testing provides the opportunity to polish the appearance of the connector, improve the experience with sensible defaults, and so on. However, this does not diminish the value of the test-driven approach. Many connector development projects have bogged down or produced hard-to-use connectors because of a failure to define tests as you define the operations, which it seems like (and is) more work up front, but does pay off – you get a better result, faster. |
Implementing Operations
The Twitter connector implements a rich set of operations; some of the simpler ones are shown below.
/**
* Returns a single status, specified by the id parameter below. The status's
* author will be returned inline. <br>
* This method calls http://api.twitter.com/1.1/statuses/show
* <p/>
* {@sample.xml ../../../doc/twitter-connector.xml.sample twitter:showStatus}
*
* @param id the numerical ID of the status you're trying to retrieve
* @return a single {@link Status}
* @throws twitter4j.TwitterException when Twitter service or network is unavailable
* @see <a href="http://dev.twitter.com/doc/get/statuses/show/:id">GET
* statuses/show/:id | dev.twitter.com</a>
*/
@Processor
public Status showStatus(long id) throws TwitterException {
return twitter.showStatus(id);
}
/**
* Answers user information for the authenticated user
* <p/>
* {@sample.xml ../../../doc/twitter-connector.xml.sample twitter:showUser}
*
* @return a {@link User} object
* @throws TwitterException when Twitter service or network is unavailable
*/
@Processor
public User showUser() throws TwitterException {
return twitter.showUser(twitter.getId());
}
/**
* Search for places that can be attached to a statuses/update. Given a latitude
* and a longitude pair, or and IP address, this request will return a list of
* all the valid places that can be used as the place_id when updating a status.
* <p/>
* {@sample.xml ../../../doc/twitter-connector.xml.sample twitter:searchPlaces}
*
* @param latitude latitude coordinate. Mandatory if ip is not specified
* @param longitude longitude coordinate.
* @param ip the ip. Mandatory if coordinates are not specified
* @return a {@link ResponseList} of {@link Place}
* @throws TwitterException when Twitter service or network is unavailable
*/
@Processor
public ResponseList<Place> searchPlaces(@Placement(group = "Coordinates") @Optional Double latitude,
@Placement(group = "Coordinates") @Optional Double longitude,
@Optional String ip) throws TwitterException {
return twitter.searchPlaces(createQuery(latitude, longitude, ip));
}
private GeoQuery createQuery(Double latitude, Double longitude, String ip) {
if (ip == null) {
return new GeoQuery(new GeoLocation(latitude, longitude));
}
return new GeoQuery(ip);
}Things to note:
-
All of these operations call methods on the client instance stored in the
twitterproperty. -
Annotations like @Optional, @Default, and @Placement are widely used to improve the configuration behavior of the connector and its appearance in Studio.
-
Because the authentication is all handled by the Java client and a few methods in the @Connector class noted above, no authentication-related code is included in the @Processor methods.
Creating JavaDoc and Samples for Operations
The JavaDoc for each operation includes a pointer to the sample code file` ../../../doc/twitter-connector.xml.sample`, as well as the usual @param and @return comments. DevKit will enforce the inclusion of these code samples, and will check the samples you provide against the parameters defined for those operations. See Creating DevKit Connector Documentation for details on creating the required documentation for each of your operations.
Creating Unit Tests for Operations
As you define each operation, you should create the unit tests that utilize it. The generated project skeleton created by the DevKit Maven archetype includes a unit test suite directory under ./src/test. DevKit defines a unit test framework based on JUnit.
For details on creating unit tests, see Developing DevKit Connector Tests.
Next Steps
If you are merely reviewing the different connector implementation types, you can return to Connector Attributes Operations and Data Model to review connector implementations that communicate directly with SOAP and RESTful Web services without using a pre-built client library.
Once you have implemented your connector with its operations, as well as created some documentation and a test suite, you can:
-
Return to the DevKit Shortcut to Success to continue the development process described there
-
Build out the test suite to improve coverage, based on information in Developing DevKit Connector Tests
-
Build out the documentation examples to show more samples, based on information in Creating DevKit Connector Documentation



