@Connector(name="barn", schemaVersion="1.0", friendlyName="Barn", minMuleVersion="3.6")
public class BarnConnector
{
@Configurable
private String key;
public String getKey() {
return key;
}
public void setKey(String key) {
this.key = key;
}
}Defining Connector Attributes
| DevKit is compatible only with Studio 6 and Mule 3. To build Mule 4 connectors, see the Mule SDK documentation. |
Like all Mule elements, connectors have attributes that can be assigned in the connector’s global configuration dialog.
Prerequisites
This document assumes you are familiar with the Anypoint Connector DevKit and you have already covered the connector’s authentication methods.
@Configurable Annotation
The connector’s attributes are defined using the @Configurable annotation on the class private attributes. These attributes are later assigned in the connector’s global configuration dialog. In addition to the @Configurable annotation, these attributes need public getters and setters (not shown).
-
A
@Connectorcan have any number of simple or complex@Configurableattributes. -
@Configurableattributes are mandatory from a user perspective.
For example:
XML configuration:
<barn:config name="Barn" key="myKey" doc:name="Barn"/>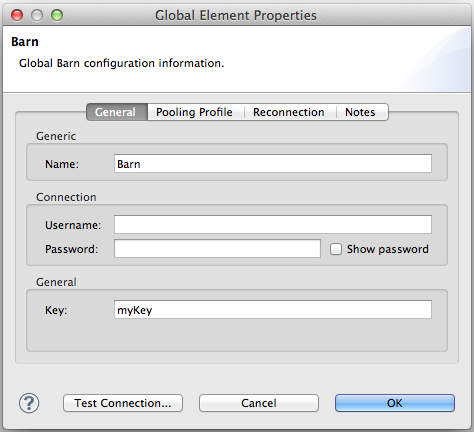
`@Optional `Annotation
As mentioned before, @Configurable attributes are mandatory. If we want to make them optional we need to mark them with the @Optional annotation.
@Connector(name="barn", schemaVersion="1.0", friendlyName="Barn", minMuleVersion="3.6")
public class BarnConnector
{
@Configurable
@Optional
private String key;
public String getKey() {
return key;
}
public void setKey(String key) {
this.key = key;
}
}XML configuration:
<barn:config name="Barn" key="myKey" doc:name="Barn"/>The following is also valid since assigning a value is optional:
<barn:config name="Barn" doc:name="Barn"/>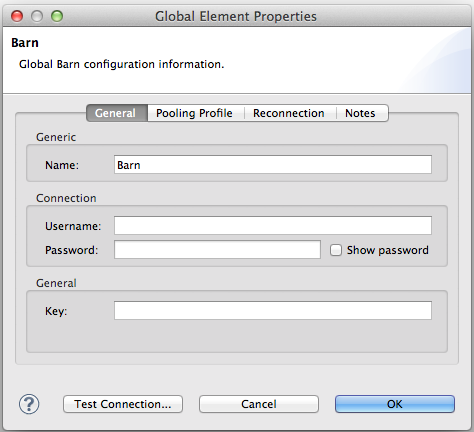
@Default Annotation
For optional attributes only, you can set a default value using the @Default annotation. This value is used if no value is assigned to the attribute.
For example:
@Connector(name="barn", schemaVersion="1.0", friendlyName="Barn", minMuleVersion="3.6")
public class BarnConnector
{
@Configurable
@Default("testKey")
private String key;
public String getKey() {
return key;
}
public void setKey(String key) {
this.key = key;
}
}XML configuration:
<barn:config name="Barn" key="myKey" doc:name="Barn"/>If the key attribute is not present it implicitly is assigned the value testKey as defined by the @Default annotation:
<barn:config name="Barn" doc:name="Barn"/>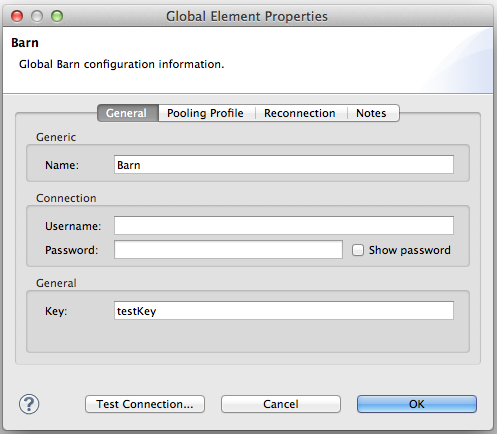
Whenever an attribute is marked as @Default, it’s implicitly @Optional as well.
|
Customizing Attributes Look and Feel
By default, Anypoint DevKit infers the names and labels for the Studio dialog boxes from methods, parameters, JavaDoc comments, and instance variable names in your Java files. However, you can also use annotations to customize many aspects of the look and feel of your component to improve the user experience.
| The package` org.mule.api.annotations.display `defines the annotations that let you perform these customizations. |
You can (and should) use several annotations that control how the attribute appears in the connector’s dialog in Studio and in your connector documentation.
`@FriendlyName `Annotation
Use this annotation to instance variables and method parameters to provide a way to override the default inferred nickname for a @Configurable variable or a @Processor/@Source/@Transformer method parameter. It is required that you provide a parameter is annotated with this.
@Connector(name="barn", schemaVersion="1.0", friendlyName="Barn", minMuleVersion="3.6")
public class BarnConnector
{
...
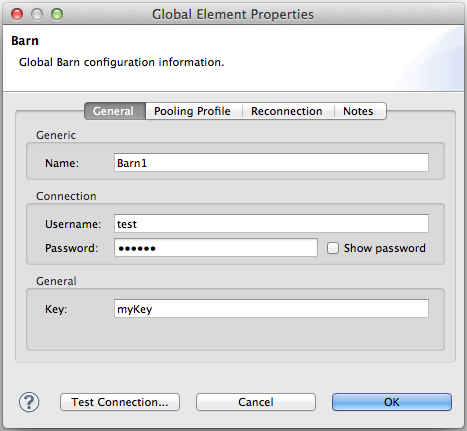
`@Password `Annotation
Use this annotation to identify a field or method parameter as a password or, more generally, as a variable which contains data that should not be displayed as plain text.
@Connect
public void connect(@ConnectionKey String username, @Password String password)
throws ConnectionException {
...
}
@Summary Annotation
Use this annotation to instance variables and method parameters to provide a way to override the default inferred description for a @Configurable variable or a @Processor/@Source/@Transformer method parameter.
@Processor
@Summary("This processor puts an animal in the barn")
public String putInBarn(String animal)
{
return animal + "has been placed in the barn";
}@Icons: Custom Palette and Flow Editor Icons
Use this annotation on the connector class to override the default location of one or more of the required icons. The path needs to be relative to /src/main/java.
@Icons(connectorLarge="barn-icon-large.png", connectorSmall="barn-icon-small.png")
@Connector(name="barn", schemaVersion="1.0", friendlyName="Barn", minMuleVersion="3.6")
public class BarnConnector
{
...@Placement: Field Order, Grouping, and Tabs
Use this annotation to instance variables and method parameters. It accepts the following parameters:
-
order — The relative order of the annotated element within its group. If the value provided is duplicated then the order of these elements is arbitrarily defined. Value is relative; an element with order 10 has higher precedence than an element with value 25.
-
group — A logical way to display one or more variables together. If you do not specify a group, then Mule assumes a default group. To place multiple elements in the same group, assign the same values to them for this attribute.
-
tab — A logical way to group annotated elements together. This attribute specifies the name of the tab in which to display the annotated element. If no tab is specified, then Mule assumes a default tab. To display multiple parameters in the same the tab, assign the same values to them for this attribute.
@Configurable
@Placement(group = "Basic Settings", order = 1)
@FriendlyName("Consumer Key")
private String consumerKey;
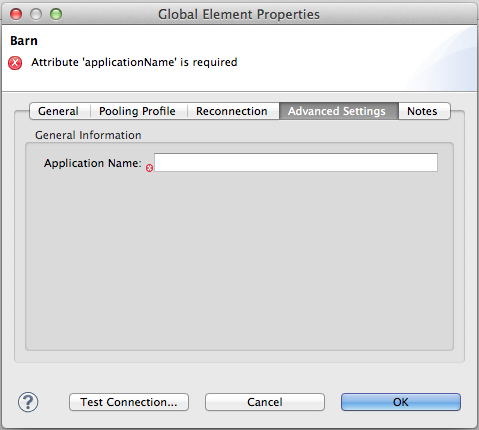
@Configurable
@Placement(tab="Advanced Settings", group = "General Information", order = 2)
@Summary("the application name")
@FriendlyName("Application Name")
private String applicationName;
@Configurable
@Placement(group = "Basic Settings", order = 3)
@FriendlyName("Consumer Secret")
@Summary("consumer secret for authentication")
private String consumerSecret;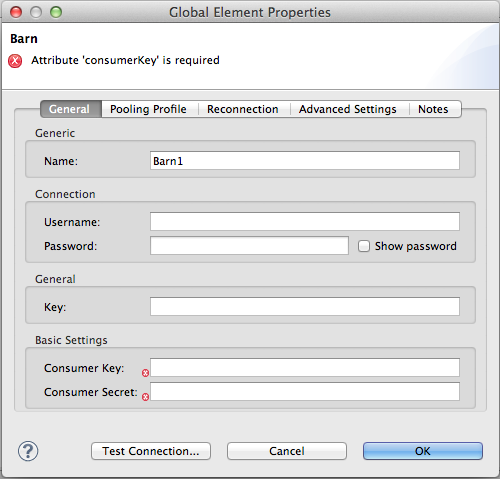
See Also
-
NEXT: Learn more about complex data types attribute support, such as enumerated types and collections.
-
Learn more about Adding DataSense to your connector.



