Implementing a REST Connector
| DevKit is compatible only with Studio 6 and Mule 3. To build Mule 4 connectors, see the Mule SDK documentation. |
Anypoint Connector DevKit provides a convenient set of annotations called @RestCall for creating a Connector for a RESTful API.
You can apply @RestCall annotations to methods (@Processor) in a Connector’s @Connector class that declaratively describes the URLs for resources exposed on the API.
The @RestCall annotation lets you perform HTTP POST, GET, PUT, and DELETE operations through its HttpMethod parameter.
At compile time, Anypoint Connector DevKit generates client code for all the operations, and provides most of the functionality for the methods. For well-defined RESTful APIs, this can be a convenient solution for quickly producing a connector.
See Also: Annotation Reference
Prerequisites
This document assumes you are familiar with RESTful APIs, and with the DevKit connector architecture described in Anypoint Connector Fundamentals.
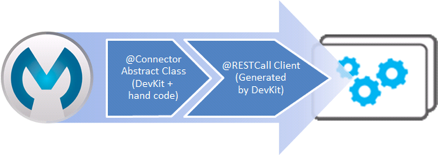
@RestCall-Based Connector Architecture
The DevKit handles "well-behaved" RESTful Web services, that is, those which require clean URLs, correct HTTP verb usage, etc.
The client is exposed through a set of annotations (the @RestCall annotations) that you apply to your @Connector class and its methods. For more information, see the Annotation Reference.
The following is the architecture of a connector built using the @RestCall annotations:

Compared to most connectors, creating REST connectors requires writing very little code. You still define a @Connector class, with properties and methods; but in this case the @Connector class and its methods are all abstract. (Any entity classes passed to the operations are still concrete classes, as with other connector types.) For each operation, apply the @RestCall annotations to provide:
-
A URI template for the target resource
-
The HTTP verb for the request
-
Any parameters to substitute into the URI or send in the query/POST body to parameterize the request
DevKit generates the entire REST client in a subclass that implements the abstract method. Developers do not see this class.
This level of simplicity is possible because the patterns for accessing a well-defined RESTful API are extremely consistent.
@RestCall Annotations
DevKit provides a set of annotations to simplify working with RESTful APIs. These annotations handle all necessary operations, generating each REST call and incorporating each REST call parameter.
@RestCall
Used with the @Processor annotation. Indicates that upon invocation, the processor makes a RESTful request.
Required arguments:
-
uri: URI of the REST resource to query
-
method: HTTP method to use
The generated code creates the URI based on the arguments passed to the @RestCall annotation, and makes a request using the verb specified by the method parameter of @RestCall.
@Processor
@RestCall(uri = "{url}/list", method = org.mule.api.annotations.rest.HttpMethod.GET)
public abstract String showAll() throws IOException;Optional arguments:
-
contentType: The content-type of the response from this method call.
@Processor @RestCall(uri = "{url}/list", method = HttpMethod.POST, contentType = "application/json") -
exceptions: A list of exceptions to throw, configured by pairing an exception type and an expression which is evaluated.
@Processor @RestCall(uri = "{url}/list", method = HttpMethod.POST, contentType = "application/json", exceptions = {@RestExceptionOn(expression="#[message.inboundProperties['http.status'] != 200]", exception = AnimalNotFoundException.class)})In this example, the
@RestExceptionOnannotation throws an exception on a specified criteria: if the HTTP status is not 200, an exception is thrown.
@RestURIParam
Allows you to dynamically generate URIs by inserting parameters which are annotated with the @RestUriParam annotation.
When applying annotations to @Processor methods, specify a placeholder in the URI by surrounding the placeholder with curly braces.
One way this can be done is by applying this annotation to @Processor methods arguments as follows:
@Processor
@RestCall(uri = "http://localhost:8089/animals/{type}", method = HttpMethod.GET)
public abstract List<Animal> listAnimalsOfType(@RestUriParam("type") String type) throws IOException;Another way is to annotate an @Configurable variable with @RestUriParam as follows:
@Configurable
@RestUriParam("url")
@Default("http://localhost:8089")
private String url;
@Processor
@RestCall(uri = "{url}/listType", method = org.mule.api.annotations.rest.HttpMethod.GET)
public abstract String getByType(@RestQueryParam("type") String type)
throws IOException;@RestQueryParam
Specifies URI query parameters, which are appended to the path of the URI after a ? or & symbol. You can apply this annotation to @Processor method arguments or to connector fields marked @Configurable. This enables you to use dynamically-generated arguments as query parameters.
Required argument: String representation of the name of the parameter to append.
@Processor
@RestCall(uri = "{url}/listType", method = HttpMethod.GET)
public abstract String getByType(@RestQueryParam("type") String type)
throws IOException;When the getByType message processor is called with mule as a parameter, the resultant call would be: http://localhost:8089/animals?type=mule
@RestHeaderParam
Allows you to insert custom headers in the HTTP request. When using this annotation, you must specify the name of the header to include in the call. As with the @RestURIParam annotation, you can apply this annotation to @Processor methods arguments or to connector fields marked @Configurable.
When annotating a specific configurable variable using the @RestHeaderParam, the variable is present in all HTTP requests.
@Configurable
@RestHeaderParam(value = "emptyHeaderField", ignoreIfEmpty = true)
private String emptyHeaderField;When you use the @RestHeaderParam on a specific argument in a method, the header is only included if the method is called.
@Processor
@RestCall(uri = "{url}/create", method = org.mule.api.annotations.rest.HttpMethod.POST)
public abstract String create(@RestHeaderParam("age") int age)
throws IOException;@RestPostParam
Allows you to set parameters in the body of POST method calls. Define the POST method with @RestCall and set its parameters with @RestPostParam.
You can apply this annotation to @Processor method arguments or to connector fields marked @Configurable. DevKit ensures that you apply this annotation only to POST methods.
Processor methods annotated with @RestPostParam cannot use a non-annotated argument or a @Payload annotated argument.
For example:
@Processor
@RestCall(uri = "http://localhost:8089/product/{name}", method = HttpMethod.POST)
public abstract Result createProduct(
@RestPostParam("name")
String name)
throws IOException;Another way is to annotate an @Configurable variable with @RestPostParam as follows:
@Configurable
@RestPostParam("category")
private String category;
@Processor
@RestCall(uri = "http://localhost:8089/product/", method = HttpMethod.POST)
public abstract Result createProduct(String name) throws IOException;See Also
For an example on how to implement a @RestCall connector, see
Creating a Connector for a RESTful API using @RESTCall Annotations



