@Connector(name="myconnector", schemaVersion="1.0", friendlyName="Connector")
public class MyConnector
{
@Config
private Config config;
public void setMyProperty(Config config)
{
this.strategy = strategy;
}
public Config getConfig()
{
return this.config;
}
...
}Configuring Connection Strategies
| DevKit is compatible only with Studio 6 and Mule 3. To build Mule 4 connectors, see the Mule SDK documentation. |
Since DevKit 3.6, connections are no longer supported at the @Connector level (excluding OAuth V1), but now are defined in a "configuration" class and injected into the @Connector.
Inject this configuration class into the connector by annotating a field in the Connector class with @Config.
This approach improves the experience for developing a connector and is the easiest way to support multiple authentication types.
Note: OAuth V1 is not supported via injection by @Config.
Prerequisites
This document assumes you are familiar with the Anypoint Connector DevKit and you are ready to implement authentication on your connector. You should also be familiar with authentication methods.
Adding @Config to a @Connector
To add a configuration class and inject it into the connector:
-
Create a new Java class for the connection strategy. This is your configuration class.
-
Annotate the class with the one of the DevKit authentication methods. In the example we are using
@ConnectionManagement. -
Develop your authentication logic or connection management.
-
Finally, in the
@Connectorannotated class, reference the connection strategy class by creating a@Configfield with the reference to the new strategy. The connector operation logic is defined separately from logic for connection with the service.
Examples
The following example shows the @Connector injecting the configuration with @Config.
This code declares the @ConnectionManagement block in the configuration file that was injected above:
@ConnectionManagement(friendlyName="Connection Management", configElementName="demo-config")
public class ConnectionManagementStrategy
{
Private Service service;
@Connect
public void connect(@ConnectionKey String username, @Password String password)
throws ConnectionException {
service = new Service(username);
try{
service.connect(password);
}catch(Exception){
throw new ConnectionException(...);
}
}
@Disconnect
public void disconnect() {
service.disconnect();
}
@ValidateConnection
public boolean isConnected() {
return service.connectionStatus();
}
@ConnectionIdentifier
public String connectionId() {
return service.getConnectionId();
}
}Supporting Multiple Authentication Models in One Connector
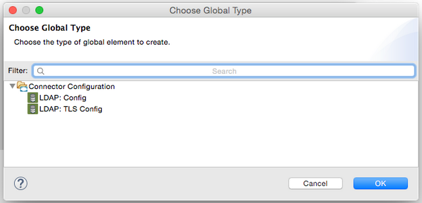
Anypoint Connector DevKit supports multiple authentication models in the same connector. The LDAP connector illustrates how to structure the connector code to support this feature.
The connector injects the base configuration type that the configurations are inherited from, AbstractConfig.
-
AbstractConfig.javais declared in one file.public abstract class AbstractConfig { ... } -
Its child classes are declared in separate files. These strategies are for caching and TLS respectively.
LDAPCacheConfig.java@ConnectionManagement(friendlyName = "Configuration", configElementName = "config") public class LDAPCacheConfig extends AbstractConfig { ... }LDAPTlsConfig.java@ConnectionManagement(friendlyName = "TLS Configuration", configElementName = "tls-config") public class LDAPTlsConfig extends AbstractConfig { ... } -
In the
LDAPConnector.javaclass, the abstract configuration is injectedpublic class LDAPConnector { ... @Config AbstractConfig config; ... }
Users can declare an abstract base class or interface using different Connection Strategies as child classes and implement the authentication logic and connection management, if applicable.
Supporting both OAuth and Basic Authentication in the same connector means having two config elements in the same XML namespace. To enable this, you can use the parameter configElementName of the Connection Strategies annotations.
For example, in the LDAP connector, the LDAPTlsConnection class sets the configElementName to tls-config , rather than the default value, config, on the other hand the LDAPCacheConnection uses the default value for configElementName. As a result, in XML, use either ldap:tls-config or ldap:config to pick the needed version of the connector. Anypoint Studio renders this when configuring the connector displaying this screen: