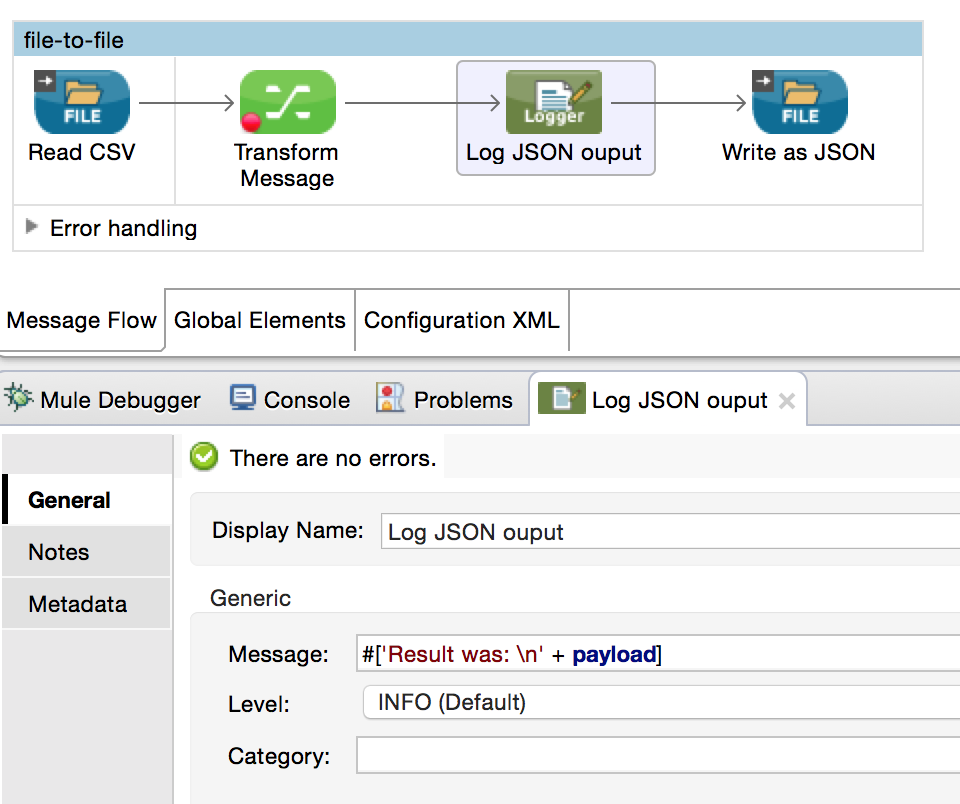
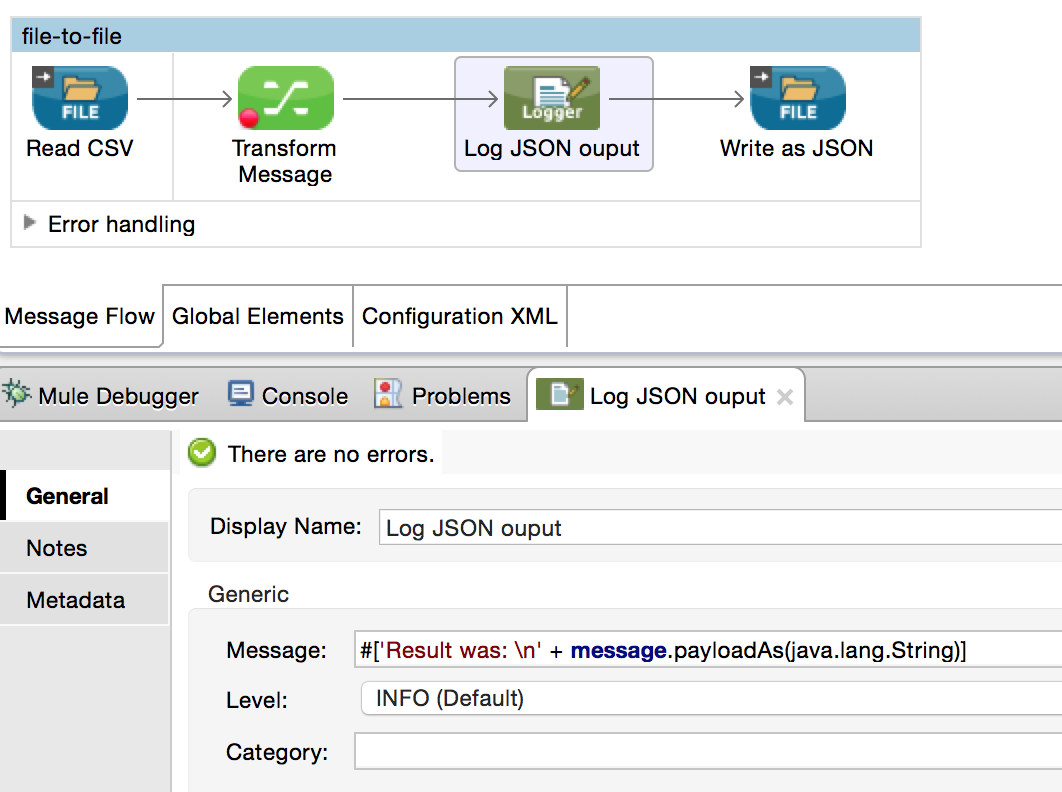
Studio Visual Editor
The example below details a CSV file input that will be processed as a stream. Its output is then written to another file in JSON format.
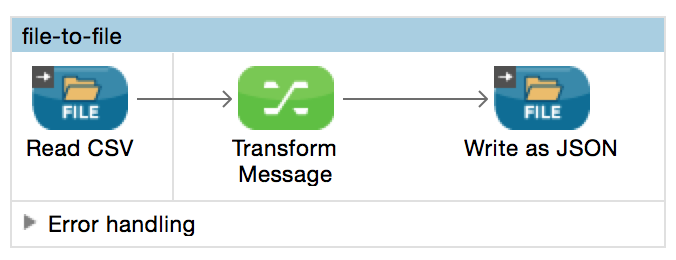
| === The File Connector automatically enables streaming. === |
XML Editor
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<mule
xmlns:file="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/file"
xmlns:dw="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/ee/dw"
xmlns="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core"
xmlns:doc="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/documentation"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core/current/mule.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/file http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/file/current/mule-file.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/ee/dw http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/ee/dw/current/dw.xsd">
<file:connector name="File" autoDelete="true" streaming="true" validateConnections="true" doc:name="File" />
<flow name="file-to-file">
<file:inbound-endpoint path="C:\input" connector-ref="File" responseTimeout="10000" doc:name="Read CSV" />
<dw:transform-message doc:name="Transform Message">
<dw:set-payload>
<![CDATA[
%dw 1.0
%output application/json
---
{
people: payload map ((payload01 , indexOfPayload01) -> {
id: payload01.id as :number,
firstName: payload01.firstName,
lastName: payload01.lastName
})
}]]>
</dw:set-payload>
</dw:transform-message>
<file:outbound-endpoint responseTimeout="10000" doc:name="Write as JSON" connector-ref="File" path="C:\output" />
</flow>
</mule>