Viewing Server Pools
| Mule Management Console (MMC) was deprecated in December 2015. Its End of Life is July 15, 2019. For more information see the MMC Migrator Tool or contact your Customer Success Manager to determine how you can migrate to Anypoint Runtime Manager. |
The Pools tab displays information about the thread pools used by this Mule ESB instance. For information on configuring thread pools in Mule, see Tuning Performance in the Mule Runtime documentation.
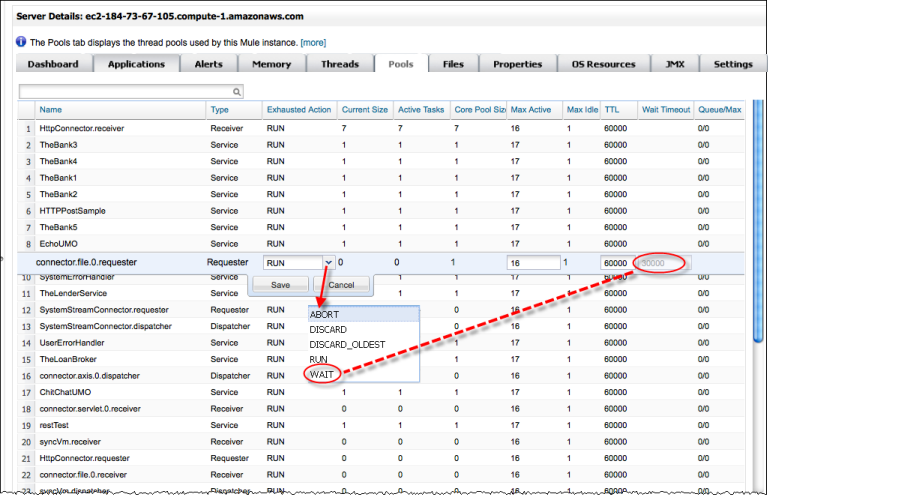
The figure below shows a typical screen displayed when the Pools tab is clicked.

Note that you can click the Exhausted Action entry for a thread pool and change the action for handling incoming tasks. When clicked, the entry displays the current action and, from the pull-down menu, you can select one of the available actions. In addition, you can modify the Max Active (the maximum number of threads used) and TTL (the length of time an inactive thread is kept in the pool) values at the same time. Click Save to record any changes you make or Cancel to discard those changes.
Note, too, that Wait Timeout values only appear for those pools whose Exhausted Action is set to Wait. However, if you click the Exhausted Action entry for a pool with an action other than Wait, the Wait Timeout value appears and, if you select Wait as the action, you can also edit wait timeout value.
The Pools tab displays the following columns:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
Name |
The name of this thread pool. This value is assigned by the application. |
Type |
The type of object using threads in this pool. |
Exhausted Action |
When the maximum pool size is reached, this value determines how to handle incoming tasks. Possible values are: WAIT (wait until a thread becomes available; don’t use this value if the minimum number of threads is zero, in which case a thread may never become available), DISCARD (throw away the current request and return), DISCARD_OLDEST (throw away the oldest request and return), ABORT (throw a RuntimeException), and RUN (the default; the thread making the execute request runs the task itself, which helps guard against lockup). |
Current Size |
The current number of threads in the pool. |
Active Tasks |
The current number of active threads. |
Core Pool Size |
The minimum number of threads kept in the pool as available for use. |
Max Active |
The maximum number of threads that will be used. |
Max Idle |
The maximum number of idle or inactive threads that can be in the pool before they are destroyed. |
TTL |
Determines how long an inactive thread is kept in the pool before being discarded. |
Wait Timeout |
How long to wait in milliseconds when the pool exhausted action is WAIT. If the value is negative, it will wait indefinitely. |
Queue/Max |
Shows how many requests are queued and the queue size when the pool is at maximum usage capacity and the pool exhausted action is WAIT. The queue is used as an overflow buffer. |



