
Choice Flow Control Reference

The Choice Flow Control, which is also known as a flow router, evaluates the payload or properties of each message it receives according to specified criteria, then determines where to route that message. Typically, two or more message processors have been designated as router targets. If more than one of these message processors meets the specified evaluation criteria, Choice routes the message to the first qualifying processor. If no message processor meets the criteria, and a message processor has been designated as the Otherwise option, the message is sent to that message processor.
In programming terms, using a Choice Flow Control adds the equivalent of an if/then/else code block to the flow logic. In the XML configuration file, the code for Choice relies on a when attribute, as the following code sample indicates:
<choice>
<when expression="payload=='foo'" evaluator="groovy">
<append-string-transformer message=" Hello foo" />
</when>
<when expression="payload=='bar'" evaluator="groovy">
<append-string-transformer message=" Hello bar" />
</when>
<otherwise>
<append-string-transformer message=" Hello ?" />
</otherwise>
</choice>You can think of a Choice Flow Control as a router that sends messages for different kinds of processing, depending on their content.
Configuring the Choice Flow Control
Complete the following steps to configure Choice Flow Control:
-
Drag the Choice icon from the Studio Palette to the Message Flow canvas, positioning it within the sequence of message blocks that form the flow (See: below, left).
-
Identify two or more message processors you want to act as potential routes (i.e., targets) for the Choice router. For example, you might want to send a message to a file or log it to a database, depending on the content of that message. One at a time, drag Logger and File to the right of the Choice icon, then release them so that they form a vertical column to the right of the Choice icon (See: below, center).
-
Double-click Choice to open its Pattern Properties pane (See: below, right).
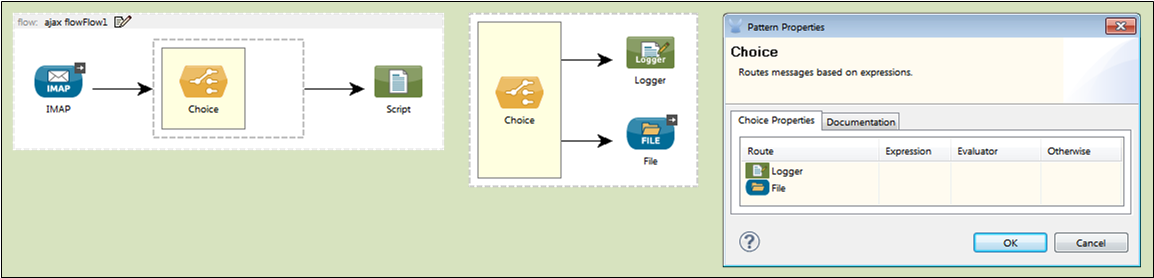
-
Click the Documentation tab and enter relevant information about this flow control, including the expression used and the available routing options, in the Description field. These notes will appear in a yellow balloon that pops up when you hover your mouse over the Choice icon on the Message Flow canvas.
The Choice Flow Control does not have a Display Name field. -
Click the Choice Properties tab to configure an evaluator and an expression for each of the routes you have specified for the Choice flow control (i.e, router).
-
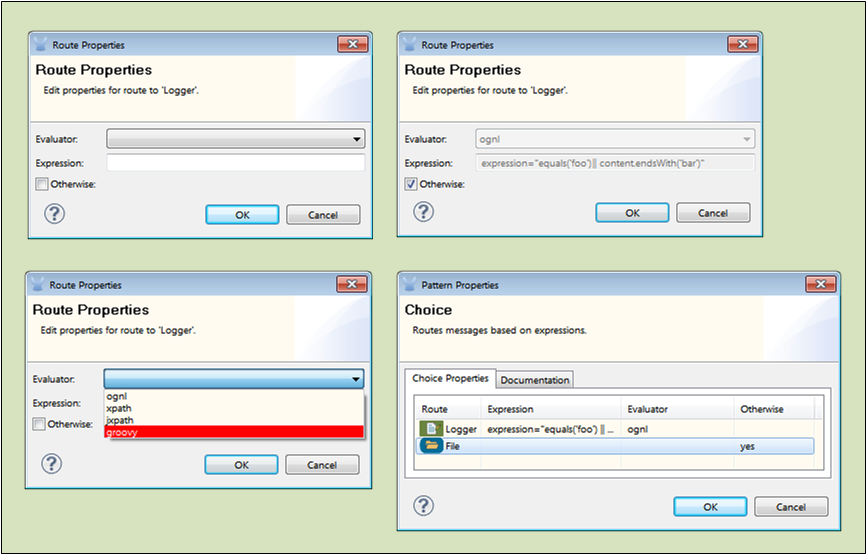
To open the Route Properties pane (See: below, upper left), double-click Logger, the first of the icons that represents a route option you specified for the Choice router. Now complete the following steps:
-
Click the down button to the right of the the Evaluator field, and select an evaluator from the drop down list (See: below, lower left). Consult Evaluator Options of the Choice Flow Control for the available choices, along with brief descriptions.
-
Enter an expression for evaluating the message. For example, you might enter something like:
expression="equals('foo') || content.endsWith('bar')" -
If you wish to designate a specific message processor as the route to be used when all other available routes fail to satisfy the expression criteria, click the check box marked Otherwise (See: below, upper right)
-
Click OK to close the Route Properties pane.
-
Repeat the previous series of steps, in turn, for each router target option in the Choice Properties pane.
| Only one route at a time can act as the Otherwise option. If you check Otherwise for more than one route, yes will appear in the Otherwise column on the Pattern Properties pane for only the the last message process designated as Otherwise (See: below, lower right). |
Evaluator Options of the Choice Flow Control
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
ognl |
An expression language for extracting, evaluating, and setting the various properties associated with Java objects. |
xpath |
A query language for locating information located on nodes within an XML tree structure and also calculating values from XML content. |
jxpath |
Not recommended. |
groovy |
A scripting language for evaluating many types of data, including Java objects. |
Mule Reference
For more information on the Choice Flow Control, see the Choice section on the Routing Message Processors page.



