Mule Messaging Styles
Mule can send messages asynchronously (each stage of the message is on a different thread) or synchronously (after the message is received by the component, it uses a single thread throughout the rest of its lifecycle and supports request-response). You can set the request-response property on the connector, on the endpoint, and implicitly within the transport.
By default, a Mule service uses SEDA, which uses asynchronous, one-way staged queues. One thread is used for the inbound message, another thread is used for processing the message in the service component, and another thread is used for the outbound message. You can configure the message so that the inbound message is on one thread and the remaining stages are on a second thread, or so that all stages are on a single thread.
Mule services also support the request-response messaging style. In this case, there is no outbound router, so the message is sent back to the same endpoint as the inbound endpoint, providing a reply back to the sender.
You can use a mix of request-response and one-way messaging styles throughout Mule services. You can also use a mix of styles for a single service component. For example, a service component can have multiple outbound routers that route to different endpoints depending on filter criteria, and you might want the message to wait for a response in some cases but not in others.
The rest of this page describes the various messaging styles in more detail and how to configure them. It includes reference to the message exchange patterns (MEPs) that each message style supports. For more information on MEPs and Mule, see [MULECDEV:MEPs].
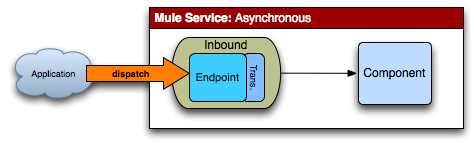
One-way

Description |
Receives a message and puts it on a SEDA queue. The callee thread returns and the message is processed by the SEDA thread pool. Nothing gets returned from the result of the call. |
Error Handling |
If an error occurs it is handled by the Mule server. An error endpoint can be used to route errors and the client that initiated the call can listen on the error queue in a separate thread, other have a specific error handling client. |
Mule Config |
The Mule service must have an asynchronous inbound endpoint. |
Equivalent MEPs |
In-only |
Discussion Points |
We have no way of supporting Robust In-only MEP outside of web services (where in Mule you would use Request/Response) and define the MEP in the service contract. |
Example Configuration
<mule xmlns="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:mule="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core"
xmlns:jms="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/jms"
xmlns:test="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/test"
xmlns:spring="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core/3.2/mule.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/test http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/test/3.2/mule-test.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/jms http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/jms/3.2/mule-jms.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<model name="Asynchronous_Message_Pattern">
<service name="AsynchronousService">
<inbound>
<jms:inbound-endpoint queue="test.in" exchange-pattern="one-way"/>
</inbound>
<test:component/>
</service>
</model>
</mule>Request Response
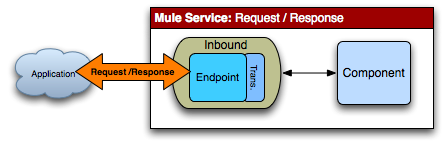
Description |
Receives a message and the component returns a message. If the component call returns null, then a |
Mule Config |
The Mule service must have a synchronous inbound endpoint and no outbound endpoint configured. You set an endpoint as synchronous using |
Error Handling |
A response message is always sent back. Clients can check the |
Equivalent MEPs |
In-Out, In-Optional-Out |
Discussion Points |
In-Optional-Out returns the request message if there is no result from the call. |
Example Configuration
<mule xmlns="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:mule="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core"
xmlns:http="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http"
xmlns:test="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/test"
xmlns:spring="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core/3.2/mule.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/test http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/test/3.2/mule-test.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http/3.2/mule-http.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<model name="Request-Response_Message_Pattern">
<service name="SynchronousService">
<inbound>
<http:inbound-endpoint host="localhost" port="8080" path="/mule/services" exchange-pattern="request-response"/>
</inbound>
<test:component/>
</service>
</model>
</mule>Synchronous
NOTE: As of 3.0, the "synchronous" flag on endpoints has been replaced by the "exchange-pattern" attribute, which has these possible values:
-
one-way
-
request-response
A message is now processed synchronously if one of the following is true:
-
endpoint is request-response
-
a transaction is active
-
the message property MULE_FORCE_SYNC is set to TRUE
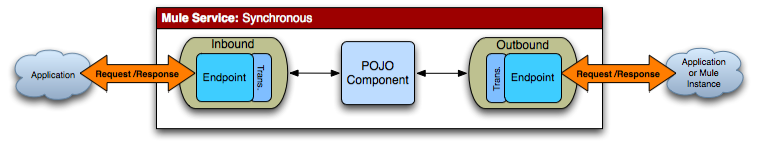
Description |
Receives a message and the component processes before sending it out on another endpoint. The request happens in the same thread. Mule blocks on the outbound endpoint to wait for a response from the remote application (if applicable) until the |
Mule Config |
The Mule service must have a request-response inbound endpoint and an outbound endpoint configured. You set an endpoint as request-response using |
Error Handling |
A response message is always sent back. Clients can check the |
Equivalent MEPs |
In-Only, In-Optional-Out, In-Out |
Discussion Points |
Mule always returns the result from the component back to the caller, as well as sending it out via the outbound endpoint. |
Example Configuration
<mule xmlns="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:mule="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core"
xmlns:jms="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/jms"
xmlns:test="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/test"
xmlns:spring="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core/3.2/mule.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/test http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/test/3.2/mule-test.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/jms http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/jms/3.2/mule-jms.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<model name="Synchronous_Message_Pattern">
<service name="SynchronousService">
<inbound>
<jms:inbound-endpoint queue="test.in" exchange-pattern="request-response"/>
</inbound>
<test:component/>
<outbound>
<pass-through-router>
<jms:outbound-endpoint queue="test.out" exchange-pattern="one-way"/>
</pass-through-router>
</outbound>
</service>
</model>
</mule>Async Request Response
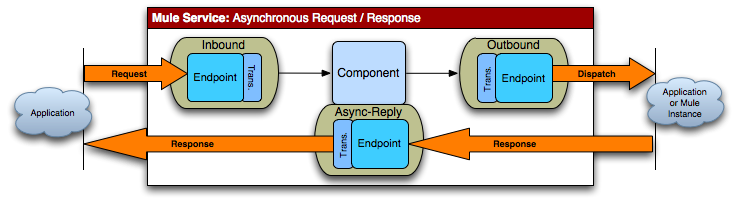
Description |
This pattern allows the back-end process to be forked to invoke other services and return a result based on the results of multiple service invocations. The Async Reply Router is used to listen on a Reply To endpoint for results. |
Mule Config |
Set the reply-to address on the outbound router, and set the <async-reply> element to listen on that reply endpoint. If you also want the caller to get a response, use a synchronous inbound endpoint by setting |
Error Handling |
A response message is always sent back. Clients can check the |
Equivalent MEPs |
In-Out, In-Optional-Out |
Discussion Points |
None |
Example Configuration
<mule xmlns="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:mule="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core"
xmlns:http="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http"
xmlns:jms="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/jms"
xmlns:test="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/test"
xmlns:scripting="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/scripting"
xmlns:spring="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core/3.2/mule.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/test http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/test/3.2/mule-test.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http/3.2/mule-http.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/jms http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/jms/3.2/mule-jms.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/scripting http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/scripting/3.2/mule-scripting.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<model name="Async_Request-Response_Message_Pattern">
<service name="AsyncRequestResponseService">
<inbound>
<http:inbound-endpoint host="localhost" port="8080" path="/mule/services"
exchange-pattern="request-response"/>
</inbound>
<test:component/>
<outbound>
<multicasting-router>
<jms:outbound-endpoint queue="service1" exchange-pattern="one-way"/>
<jms:outbound-endpoint queue="service2" exchange-pattern="one-way"/>
<reply-to address="jms://reply.queue"/>
</multicasting-router>
</outbound>
<async-reply timeout="5000">
<jms:inbound-endpoint queue="reply.queue" exchange-pattern="one-way"/>
<collection-async-reply-router/>
</async-reply>
</service>
</model>
</mule>


