HTTP Endpoint Reference
Mule uses HTTP Endpoints to send and receive requests over HTTP transport protocol, or HTTPS over the SSL protocol. Configured as either inbound (also known as message sources) or outbound, HTTP endpoints use one of two message exchange patterns: request-response or one-way.
To learn more about endpoints, refer to the Studio Endpoints document.
Configuration
Complete the following procedure to add an HTTP endpoint to a flow in your Mule application.
-
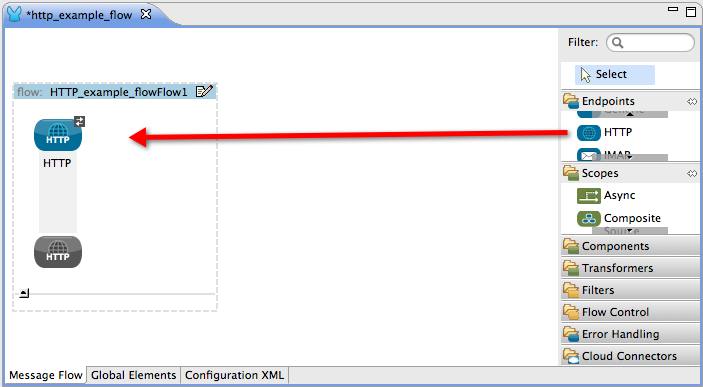
In Studio, drag the HTTP icon from the Studio palette to the canvas. Position the endpoint at the beginning of a flow to use it as an inbound endpoint (see image below). Position the endpoint anywhere else in the flow to use it as an outbound endpoint.
Alternatively, add a<http:inbound-endpoint>or<http:outbound-endpoint>element to the XML configuration (see code below).
<http:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="request-response" host="localhost" port="8081" doc:name="HTTP"/><http:outbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="one-way" host="localhost" port="8081" doc:name="HTTP"/> -
Double click the HTTP building block to open its Pattern Properties panel (below).
image::open-properties.png[open_properties] -
Refer to the sub-sections below to configure the HTTP endpoint within the tabs in the pattern properties panel.
General Tab
-
In the Display Name field, enter a name for the endpoint (refer to image above).
Alternatively, change the value of thedoc:nameattribute of the HTTP endpoint element in the XML configuration (see code below).<http:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="request-response" host="localhost" port="8081" doc:name="TalkToMe"/> -
Click a radio button to select a message exchange pattern.
Alternatively, change the value of theexchange-patternattribute of the HTTP endpoint element in the XML configuration.One-Way vs. Request-Response
Notice that the HTTP endpoint has a request-response message exchange pattern (as indicated by the small double-arrow icon — below, left). When it must respond to a requester, the HTTP endpoint has a request-response message exchange pattern.
If an HTTP endpoint has only to input information into an application, it requires a one-way message exchange pattern (below, right).

-
Check the Enable HTTPS box to send HTTPS over SSL protocol.
Alternatively, add an emptyconnector-refattribute to the HTTP endpoint element in the XML configuration (see code below).<https:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="request-response" host="localhost" port="8081" doc:name="TalkToMe" connector-ref=""/>If you enable HTTPS, ensure that you configure, then reference a References Tab on your endpoint. -
In the Host field, enter the location of the host server to which the HTTP must connect. Enter the location as a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) or an IP address.
Alternatively, change the value of thehostattribute of the HTTP endpoint element in the XML configuration. -
In the Port field, enter a number to identify the port through which the HTTP endpoint must connect to the host server (for example,
8081).
Alternatively, change the value of theportattribute of the HTTP endpoint element in the XML configuration. -
In the Path field, specify the location in the host domain to which the HTTP must connect.
Alternatively, add apathattribute to the HTTP endpoint element in the XML configuration (see code below).
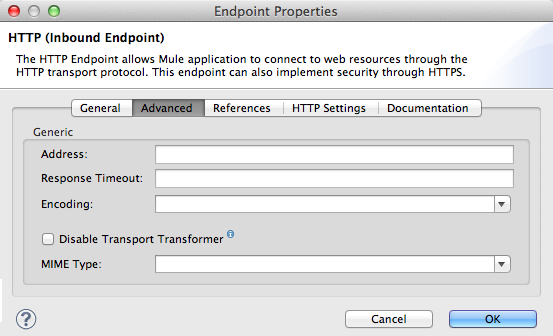
<https:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="request-response" host="localhost" port="8081" doc:name="TalkToMe" connector-ref="" path="/transports/graphics"/>Advanced Tab
-
In the Address field, enter the complete URI location of the host server to which the HTTP must connect.
Alternatively, add an
addressattribute to the HTTP endpoint element in the XML configuration (see code below).<http:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="request-response" doc:name="TalkToMe" address="http://localhost:8081/file"/>Host and Path, or Address?
If you enter the URI for the host server in the Address field, you don’t need to enter any information in the Host and Path fields. Similarly, if you entered host server information in the Host and Path fields, you don’t need to enter a URI in the Address field.
Apply either the Host and Path attributes, OR the Address attribute to an HTTP endpoint.
-
In the Response Timeout field, enter a number to indicate the amount of time (millisecond) the endpoint should wait before ending a synchronous endpoint call.
Alternatively, add aresponseTimeoutattribute to the HTTP endpoint element in the XML configuration (see code below).<http:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="request-response" doc:name="TalkToMe" address="http://localhost:8081/file" responseTimeout="340000"/> -
Use the drop-down box in the Encoding field to identify the string encoding for a message.
Alternatively, add an
encodingattribute to the HTTP endpoint element in the XML configuration (see code below).<http:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="request-response" doc:name="TalkToMe" address="http://localhost:8081/file" responseTimeout="340000" encoding="ISO-8859-1"/> -
Check the Disable Transport Transformer box to prevent Mule from automatically applying any transformations to a message it receives.
Alternatively, add adisableTransportTransformerattribute to the HTTP endpoint element in the XML configuration (see code below).<http:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="request-response" doc:name="TalkToMe" address="http://localhost:8081/file" responseTimeout="340000" encoding="ISO-8859-1" disableTransportTransformer="true"/>To facilitate processing, an HTTP endpoint in Mule automatically applies default transformations to messages it receives. These default transformations make the message contents more “Mule friendly”.
However, if you want the HTTP endpoint to strictly maintain the data format of messages it receives, check the Disable Transport Transformer box.
-
Set the MIME Type to specify the type of messages the HTTP endpoint handles. For example, set the MIME type to
text/HTMLon HTTP endpoints to handle plain text messages.
Alternatively, add amimeTypeattribute to the HTTP endpoint element in the XML configuration (see code below).
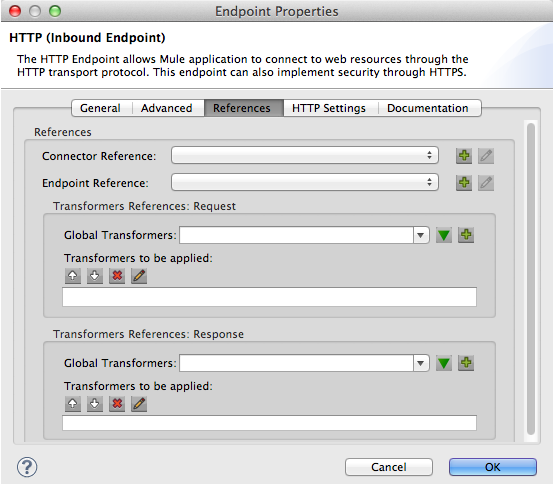
<http:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="request-response" doc:name="TalkToMe" address="http://localhost:8081/file" responseTimeout="340000" encoding="ISO-8859-1" disableTransportTransformer="true" mimeType="text/javascript/>References Tab
-
In the Connector Reference field, use the combo-box to select a Global Connector for the HTTP endpoint to reference. The endpoint uses the connector configurations you define within the global connector.
Alternatively, add aconnector-refattribute to the HTTP endpoint element in the XML configuration (see code below).<http:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="request-response" doc:name="TalkToMe" address="http://localhost:8081/file" responseTimeout="340000" encoding="ISO-8859-1" connector-ref="HTTP_Polling" disableTransportTransformer="true" mimeType="text/javascript/>What is a Global Connector?
Mule ESB uses Global Elements, like the HTTP/HTTP Connector, the HTTP Polling Connector and the String to Email Transformer, to specify transport details or set reusable configurations.
Rather than repeatedly write the same code to apply the same configuration to multiple message processors, you can create one global element that details your configurations or transport details. Then, instruct any number of message processors in your Mule application to reference that global element.
Global transport configurations do not exist within a Mule flow. Rather, the configurations reside in a global connector on the Global Elements tab on the Studio canvas, or at the top of the application in the XML configuration. An HTTP endpoint in a flow simply references a global connector to obtain transport configuration details.
-
In the Endpoint Reference field, use the combo-box to select a global endpoint for the HTTP endpoint to reference. The endpoint uses the configurations you define within the global connector.
Alternatively, add arefattribute to the HTTP endpoint element in the XML configuration (see code below).<http:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="request-response" doc:name="TalkToMe" address="http://localhost:8081/file" responseTimeout="340000" encoding="ISO-8859-1" connector-ref="HTTP_Polling" disableTransportTransformer="true" mimeType="text/javascript/ ref="HTTP"/> -
In the Transformers References: Request section, use the drop-down box in the Global Transformers field to select a global transformer for the HTTP endpoint to reference (see image below). The endpoint uses the configurations you define within the global transformer to convert the data format of a request.
image::drop-down-select.png[drop_down_select] -
Click the green arrow button to move your global transformer selection to the Transformers to be applied list below. Mule applies this transformation to the request before sending it to the transport.
image::move-one-down.png[move_one_down] -
Repeat the preceding two steps to add multiple transformations. Use the up and down arrows to reorder transformations in the Transformers to be applied list.
image::reorder.png[]Alternatively, add a
transformer-refsattribute to the HTTP endpoint element in the XML configuration (see code below).<http:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="request-response" doc:name="TalkToMe" address="http://localhost:8081/file" responseTimeout="340000" encoding="ISO-8859-1" connector-ref="HTTP_Polling" disableTransportTransformer="true" mimeType="text/javascript/ ref="HTTP" transformer-refs="Byte_Array_to_String String_to_Email"/> -
In the Transformers References: Response section, use the drop-down box in the Global Transformers field to select a global transformer for the HTTP endpoint to reference. The endpoint uses the configurations you define within the global transformer to convert the data format of a response.
-
Click the green arrow button to move your global transformer selection to the Transformers to be applied list below. Mule applies the transformation to the response before sending it to the transport.
-
Repeat the preceding two steps to add multiple transformations. Use the up and down arrows to reorder transformations in the Transformers to be applied list.
Alternatively, add aresponseTransformer-refsattribute to the HTTP endpoint element in the XML configuration (see code below).
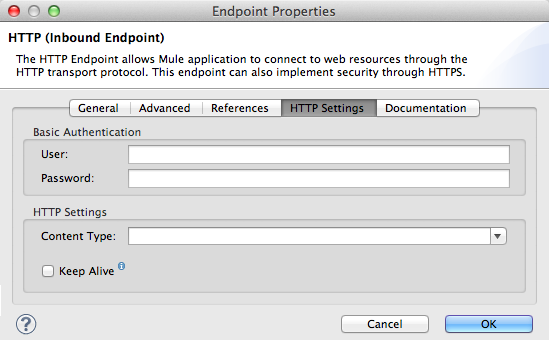
<http:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="request-response" doc:name="TalkToMe" address="http://localhost:8081/file" responseTimeout="340000" encoding="ISO-8859-1" connector-ref="HTTP_Polling" disableTransportTransformer="true" mimeType="text/javascript/ ref="HTTP" transformer-refs="Byte_Array_to_String String_to_Email" responseTransformer-refs="String_to_Email"/>HTTP Settings Tab
-
In the User and Password fields, type the username and password, respectively, that the HTTP endpoint uses to identify itself to the host server.
Alternatively, adduserandpasswordattributes to the HTTP endpoint element in the XML configuration (see code below).<http:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="request-response" doc:name="TalkToMe" address="http://localhost:8081/file" responseTimeout="340000" encoding="ISO-8859-1" connector-ref="HTTP_Polling" disableTransportTransformer="true" mimeType="text/javascript/ ref="HTTP" transformer-refs="Byte_Array_to_String String_to_Email" user="user1213" responseTransformer-refs="String_to_Email"/> -
In the Content Type field, use the drop-down box to select the type of content the HTTP request or response contains.
Alternatively, add acontentTypeattribute to the HTTP endpoint element in the XML configuration (see code below).<http:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="request-response" doc:name="TalkToMe" address="http://localhost:8081/file" responseTimeout="340000" encoding="ISO-8859-1" connector-ref="HTTP_Polling" contentType="text/html"disableTransportTransformer="true" mimeType="text/javascript/ password="testing" ref="HTTP" transformer-refs="Byte_Array_to_String String_to_Email" user="user1213" responseTransformer-refs="String_to_Email"/> -
Check the Keep Alive box to maintain an open socket connection when a small interruption occurs.
Alternatively, add akeep-aliveattribute to the HTTP endpoint element in the XML configuration (see code below).<http:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="request-response" doc:name="TalkToMe" address="http://localhost:8081/file" responseTimeout="340000" encoding="ISO-8859-1" connector-ref="HTTP_Polling" contentType="text/html" disableTransportTransformer="true" keep-alive="true" mimeType="text/javascript/ password="testing" ref="HTTP" transformer-refs="Byte_Array_to_String String_to_Email" user="user1213" responseTransformer-refs="String_to_Email"/>
Documentation Tab
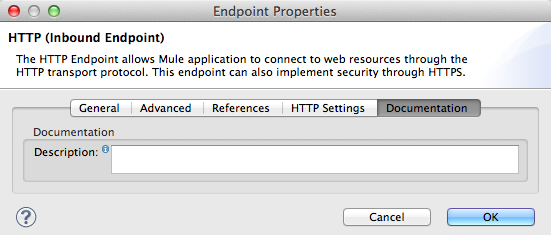
-
In the Description field, add text to describe the function of the HTTP endpoint in your Mule flow.
Alternatively, add adoc:descriptionattribute to the HTTP endpoint element in the XML configuration (see code below).<http:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="request-response" doc:name="TalkToMe" address="http://localhost:8081/file" responseTimeout="340000" encoding="ISO-8859-1" connector-ref="HTTP_Polling" contentType="text/html" disableTransportTransformer="true" doc:description="Lorem ipsum" keep-alive="true" mimeType="text/javascript/ password="testing" ref="HTTP" transformer-refs="Byte_Array_to_String String_to_Email" user="user1213" responseTransformer-refs="String_to_Email"/> -
Click OK to save your HTTP configuration changes.



