Mule Message Encryption Processor
Encrypting a Message Payload
Add a Mule Message Encryption Processor to a flow to change the content of a message so that it becomes unreadable by other entities. Mule can encrypt the entire payload of a message or specific parts of the payload, according to security requirements, using one of the following three Encryption Strategies:
| Encryption Strategy | Characteristics |
|---|---|
JCE Encrypter |
• encrypts stream, byte[] or string |
XML Encrypter |
• encrypts string |
PGP Encrypter |
• encrypts stream, byte[] or string |
JCE Encrypter
As Mule’s default encryption strategy, the Java Cryptology Extension (JCE) encrypter encodes a message payload, or part of a payload, according to the configurations of the following attributes:
-
a plain key
-
a key password
-
a keystore
-
a keystore password
-
an algorithm (19 available, refer to Appendix)
-
an encryption mode
To encrypt the payload of a message you must, at minimum, set the operation, encrypter, and the key, as well as create a basic Encryption global element. The key is the parameter to the encryption algorithm that determines the functional output of encryption or decryption. Without it, the encryption/decryption algorithm would not produce usable output.
To ensure functionality, Mule automatically applies the following default values to the message encryption configuration:
However, you can configure any of the other attributes — all of which are optional — to define Mule’s encryption settings.
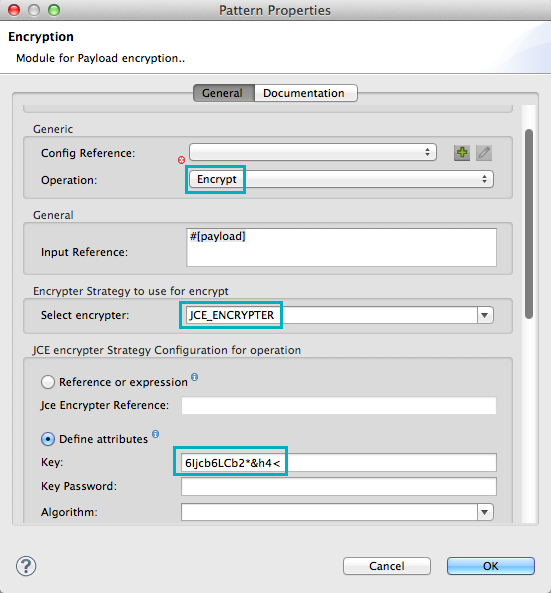
Configure the Encryption building block in the visual editor by opening the Properties window, shown below.
-
Set the Operation field to
Encrypt. -
Select
JCE_ENCRYPTERfrom the Select encrypter drop-down menu. -
Select the Define attributes radio button.
-
Enter a key in the Key field.

Or, configure the Encryption building block in the XML editor, as shown below:
<encryption:config >
<encryption:jce-encrypter key="6Ijcb6LCb2*&h4<"/>
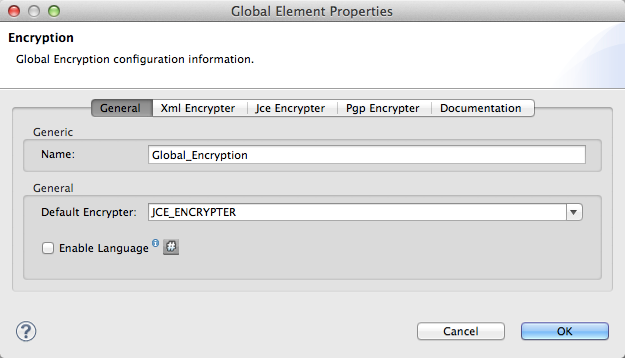
</encryption:config>Next, create an Encryption global element by clicking the  icon next to the Config Reference field. In the Global Element Properties window:
icon next to the Config Reference field. In the Global Element Properties window:
-
Enter a Name for the global element.
-
In the Default Encrypter field, select
JCE_ENCRYTPER. -
At this point, you can click OK to save this simple global Encrytper element, with no further configurations. If you do, Mule uses the configurations you defined in your local Encrypter message processor. However, if you wish to use a keystore, click the Jce Encrypter tab.
-
Select one of two radio buttons to configure the attributes of the Global element:
-
select the Reference or expression radio button to use an expression to reference attributes you have defined elsewhere in the XML configuration of your applications, or to reference the configurations defined in a bean.
-
select Define attributes to manually assign values to the attributes. Note that you can define all the attributes – except for Keystore Path and Keystore Password – in the local Encryption message processor, if you prefer.
-
XML Encrypter
The XML encrypter encodes XML string content in a message payload according to the configurations of the following attributes:
-
key
-
key password
-
xpath (use to specify a particular part of a payload to encrypt)
-
algorithm (four available: AES-128, AES-192, AES-256, Triple DES)
To encrypt the payload of a message you must, at minimum, set the operation, encrypter, and the key, as well as create a basic Encryption global element. Configure these in the visual editor (as described above for the JCE encrypter) or via XML code (shown below). By default, Mule automatically applies the AES-256 algorithm and encrypts the entire message payload.
<encryption:config >
<encryption:xml-encrypter key="pNVDBAtJ8S8mXfHc"/>
</encryption:config>However, you can configure any of the other three attributes — all of which are optional — to define Mule’s encryption settings.
PGP Encrypter
Mule has the ability to encrypt a message payload, or part of a payload, using Pretty Good Privacy (PGP). Because of its increased complexity, the topic has earned its own page: refer to the PGP Encrypter document.
Encrypting Part of a Message Payload
For details on message encryption in Mule, refer to the Encrypt a Message Payload section above.
By default, when you apply an encrypter, Mule encrypts the entire message payload. However, you can use a Mule Expression to encrypt a specific part of a message rather than the whole payload. Configure the Input Reference to define the specific part(s) of the payload you wish to encrypt.
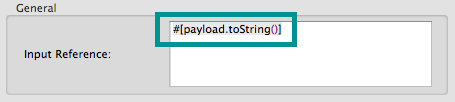
Additionally, you can add an Xpath expression attribute to the XML encrypter to define specific field(s) to encrypt — credit card number or SSN, for example (see below).
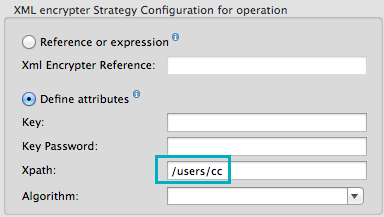
<encryption:encrypt doc:name="Encrypt CC" using="XML_ENCRYPTER" config-ref="plainXML" input-ref="#[payload.toString()]">
<encryption:xml-encrypter xpath="/users/cc"/>
</encryption:encrypt>Decrypting a Message Payload
Add a Mule Message Encryption Processor to decrypt the content of a message so that it becomes readable by the message processors in your Mule application. Mule can decrypt the entire payload of a message or specific parts of the payload using one of the following three Encryption Strategies:
-
JCE Decrypter
-
PGP Decrypter
-
XML Decrypter
Refer to Encrypt a Message Payload document for details on the Encryption strategies.
The type of encryption strategy you use to decrypt a message depends entirely upon the type of encryption employed by the message sender.
Further, you must configure a decrypter’s attributes to address the type of encryption the message’s sender applied. For example, if the message uses a keystore for encryption, your decrypter must use the keystore to decrypt the message.
Decrypting Part of a Message Payload
Refer to the Decrypting a Message Payload section for details on message decryption in Mule.
By default, Mule decrypts the entire message payload when you apply a decrypter. However, you can use a Mule Expression to decrypt a specific part of a message payload rather than the whole payload. Configure the Input Expression to define the specific part(s) of the payload you wish to decrypt.
Additionally, you can add an Xpath expression attribute to the XML decrypter to define specific field(s) to decrypt — credit card number or SSN, for example (refer to the encryption screenshot and code in Encrypt Part of a Message Payload).
Next Steps
Examine the Anypoint Enterprise Security Example Application which illustrates how to encrypt and decrypt a message in a Mule flow.
Appendix
| Algorithms Available in JCE | Minimum Key Size |
Maximum Key Size |
|---|---|---|
AES |
16 |
16 |
Blowfish |
1 |
Unlimited |
DES |
8 |
8 |
DESede |
16 |
24 |
Camellia |
16 |
16 |
CAST5 |
1 |
16 |
CAST6 |
1 |
Unlimited |
Noekeon |
16 |
Unlimited |
Rijndael |
16 |
16 |
SEED |
16 |
Unlimited |
Serpent |
16 |
16 |
Skipjack |
16 |
Unlimited |
TEA |
16 |
Unlimited |
Twofish |
8 |
Unlimited |
XTEA |
16 |
Unlimited |
RC2 |
1 |
Unlimited |
RC5 |
1 |
Unlimited |
RC6 |
1 |
Unlimited |
RSA |
16 |
Unlimited |
See Also
-
Read more about encryption in Mule Studio in our MuleSoft Blog.



