Choosing Between MEL and CTL2 for DataMapper Scripting
The transformation code for Anypoint DataMapper element mappings can be generated in one of two languages: Mule Expression Language (MEL) or CTL2 (Clover Transformation Language).
As of Mule 3.4, MEL is the default language, MEL offers a number of technical advantages over CTL2.
-
MEL can call out to any Java library. For example, you have the usual Java string and mathematical functions available, as well as any Java library you include in your project.
-
MEL is used throughout the rest of Mule as the primary expression language, so using it in DataMapper makes for an experience more consistent with the rest of Mule ESB.
-
MEL is being actively developed with new capabilities to continue to expose Mule features.
Mule recommends that you use MEL rather than CTL2 for future DataMapper development.
CTL2 was licensed from a third party for use in the past versions of DataMapper, and is still fully supported for reasons of backward compatibility, but it offers no functional advantages over MEL. Note, when using MEL in DataMapper, the Mule message object is not available for use.
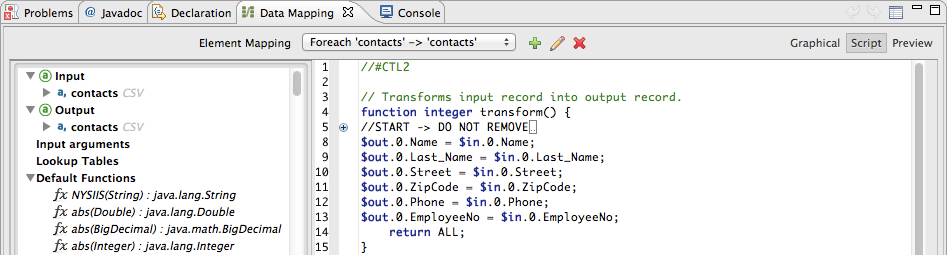
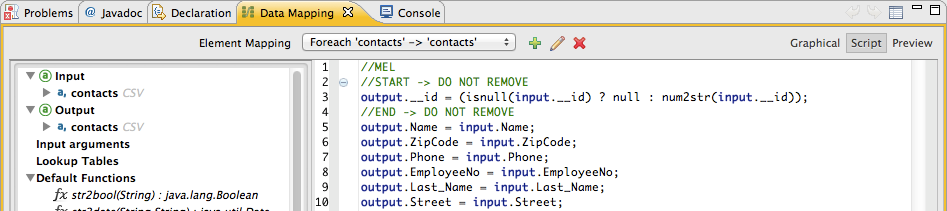
The images below illustrate DataMapper’s [Script view] displaying the same mapping, in CTL2 (below, at top) and MEL (below, at bottom).

Setting the DataMapper Scripting Language Preference
By default, Studio uses MEL as DataMapper’s scripting engine. However, you can change this setting if you wish to use CTL2 as the default.
-
In Studio, navigate to Preferences > Mule Studio > DataMapper.
-
Use the drop-down for the Default Script Type field to select
CTL2.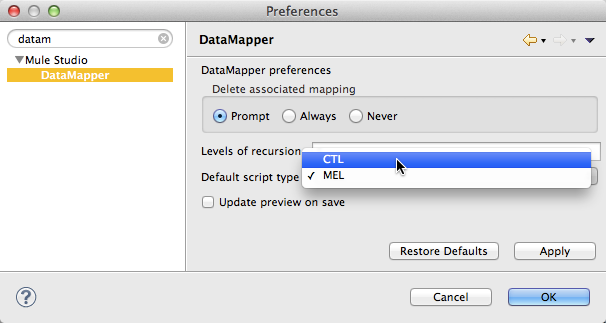
-
Click OK to save your changes.
See Also
-
For complete information on MEL, see Mule Expression Language



