doc:name="HTTP Static Resource Handler"HTTP Static Resource Handler
| Mule Runtime Engine versions 3.5, 3.6, and 3.7 reached End of Life on or before January 25, 2020. For more information, contact your Customer Success Manager to determine how you can migrate to the latest Mule version. |
Use the HTTP Static Resource Handler to specify any HTTP static resource as an output.
Configuration with Anypoint Studio Visual Editor
Insert the HTTP Static Resource Handler into your flow and configure it per the following table.
| Field | Description | Default Value | Sample XML |
|---|---|---|---|
Display Name |
Name of the component as it appears in the flow. |
HTTP Static Resource Handler |
|
Resource Base |
Required. The resource folder where the html document(s) are stored. |
N/A |
|
Default File |
Required. The default main file to serve when the directory is specified. If no file is specified, index.html will be used. |
index.html |
|
Configuration with Anypoint Studio XML Editor or Standalone
<http:static-resource-handler resourceBase="/myApp" doc:name="HTTP Static Resource Handler" defaultFile="index.html"/>| Element | Description |
|---|---|
http:static-resource-handler |
Specify any HTTP static resource to be the output produced by this component. |
| Attribute Name | Description | Type | Default Value | Sample XML |
|---|---|---|---|---|
resourceBase |
Required. The resource folder where documents are stored. |
string |
N/A |
|
defaultFile |
Required. The default main file to serve when the directory is specified. |
string |
index.html |
|
doc:name |
Customize to display a unique name for the logger in your application. Note: Attribute not required in Mule Standalone configuration. |
string |
N/A |
|
Example Implementation with Anypoint Studio Visual Editor
-
Drag an HTTP connector into a new flow, followed by an HTTP Static Resource Handler.
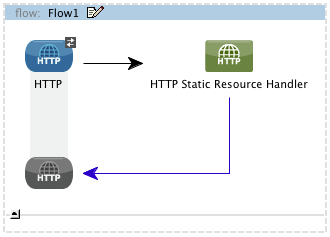
-
Leave the HTTP connector with its default settings, pointing to
localhost:8081. -
Create a new folder on your local hard drive, then place a static html file in it. Any html file will do.
-
Configure the HTTP Static Resource Handler to reference the folder and file. In this example, the path is /Users/aaron/Desktop/Input and the file name is mulesoft.html.
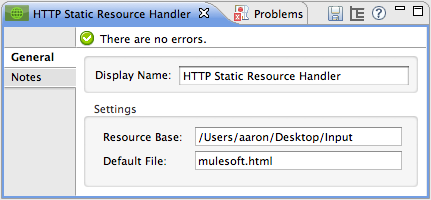
-
Save, then run your project.
-
Open any browser window, then type
localhost:8081/mulesoft.htmlinto the address bar (or whatever your html file is named). -
Your HTML file loads.
The payload produced by this component is the HTTP content of the mulesoft.html file. The folder specified in the Resource Base may also contain other files such as .css stylesheets or .js scripts that the main .html file can reference.
Example Implementation with Anypoint Studio XML Editor or Standalone
-
Create a new flow and add an HTTP inbound endpoint. Set the host to localhost and the port to 8081.
<flow name="Flow1" doc:name="Flow1"> <http:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="request-response" host="localhost" port="8081" doc:name="HTTP"/> </flow> -
Create a new folder on your local hard drive, then place any static html file in that folder. In this example, the path is /Users/aaron/Desktop/Input and the file name is mulesoft.html.
-
Add a HTTP Static Resource Handler and configure it to reference this file.
<flow name="Flow1" doc:name="Flow1"> <http:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="request-response" host="localhost" port="8081" doc:name="HTTP"/> <http:static-resource-handler resourceBase="/Users/aaron/Desktop/Input" doc:name="HTTP Static Resource Handler" defaultFile="mulesoft.html"/> </flow> -
Save, then run your project.
-
Open any browser window, then type
localhost:8081/mulesoft.htmlinto the address bar (or whatever your html file is named).
The payload produced by this component is the HTTP content of the mulesoft.html file. The folder specified in the Resource Base may also contain other files such as .css stylesheets or .js scripts that the main .html file can reference.
Complete Example Code
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<mule xmlns:http="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http" xmlns="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core" xmlns:doc="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/documentation" xmlns:spring="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-current.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core/current/mule.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http/current/mule-http.xsd">
<flow name="http_static_resource_handler_testFlow1" doc:name="http_static_resource_handler_testFlow1">
<http:inbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="request-response" host="localhost" port="8081" doc:name="HTTP"/>
<http:static-resource-handler resourceBase="${app.home}/web" defaultFile="index.html" doc:name="HTTP Static Resource Handler"/>
</flow>
</mule>
In this example, the resource handler deals with documents in the project folder src/main/app/web, referenced dynamically through the expression ${app.home}/web
|
See Also
-
Add some conditional logic to your flow routers.



