Mule CRC32 Processor
| Mule Runtime Engine versions 3.5, 3.6, and 3.7 reached End of Life on or before January 25, 2020. For more information, contact your Customer Success Manager to determine how you can migrate to the latest Mule version. |
Mule can apply a cyclic redundancy check (CRC) to messages to ensure integrity. The CRC32 processor acts as an enricher to generate a checksum to a message when it enters a system, then act as a filter to verify the checksum when the message leaves the system. If the entry and exit values do not match, CRC terminates the message’s processing.
The CRC32 processor allows the user to verify that a message remains intact between a sender and a receiver. Because it does not itself provide encryption or append a signature to the message, you can use it in conjunction with other security features.
Generating a Checksum
To use the CRC32 processor to generate a checksum on a message, you must, at minimum, configure two elements in your Mule application:
-
Global CRC32 element
-
CRC32 processor
Completing these steps ensures that Mule calculates a checksum based on your payload and enriches the properties of your Mule message with that checksum.
Creating a Global Element with Studio Visual Editor
-
Create and configure the global element through the Global Element tab at the bottom of the canvas, or directly within the CRC32 building block’s Properties pane by clicking the
 icon to the right of the Connector Ref field.
icon to the right of the Connector Ref field. -
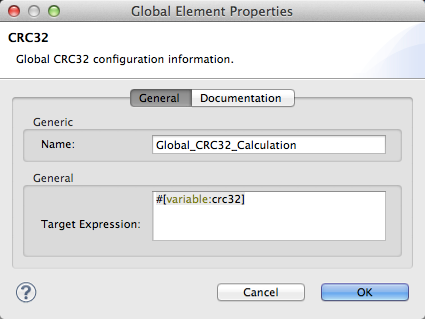
Configure the global element’s attributes according to the table below.

Attribute Req’d Value Name
x
A unique name for your global element.
Target Expression
x
A Mule expression, accept the default variable name
#[variable:crc32]
Creating a Global Element with Studio XML Editor or Standalone
-
Create a
crc32:configelement, set above all the flows in your application. -
Configure the global element’s attributes according to the table below.
<crc32:config name="Global_CRC32_Calculation" targetExpression="#[variable:crc32]/>Attribute Req’d Value name
x
A unique name for your global element.
targetExpression
x
A Mule expression, accept the default variable name `#[variable:crc32] `
Configuring a CRC32 Message Processor with Studio Visual Editor
-
Insert a CRC32 processor in your Mule flow.
-
Configure the message processor’s attributes according to the table below.
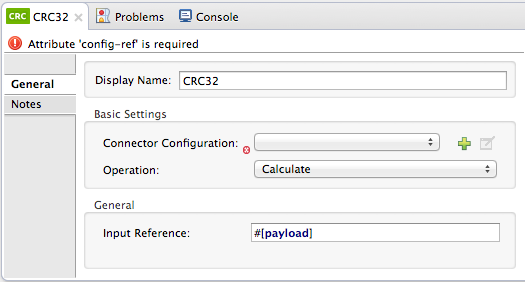
Attribute Req’d Value Display Name
x
A unique name for your message processor.
Connector Configuration
x
Use the global element you created above.
Operation
x
Calculate
Input Reference
By default, Mule calculates based on the entire payload. Use the Input Reference field to specify a different target for the calculation, if necessary.
Configuring a CRC32 Message Processor with Studio XML Editor or Standalone
-
Insert a
crc32:calculateprocessor in your Mule flow. -
Configure the element’s attributes according to the table below.
<crc32:calculate config-ref="Global_CRC32_Calculation" doc:name="CRC Calculation"/>Attribute Req’d Value config-ref
x
Use the global element you created above.
doc:name
x
A display name for the element in Studio’s Visual Editor. Not applicable for Standalone.
input-ref
By default, Mule calculates based on the entire payload. Use input-ref to specify a different target for the calculation, if necessary.
Verifying a Checksum
To use the CRC32 processor to verify a checksum on a message, you must, at minimum, configure two elements in your Mule application:
-
CRC32 message processor
-
CRC32 global element
Completing these steps ensure that Mule verifies the checksum in the properties of your message by comparing it against the checksum you calculated in the CRC32 calculation, Generating a Checksum.
Configuring a CRC32 Message Processor with Studio Visual Editor
-
Insert a CRC32 processor into your Mule flow, positioned at the point where you would like to verify the checksum.
-
Configure the message processor’s attributes according to the table below.
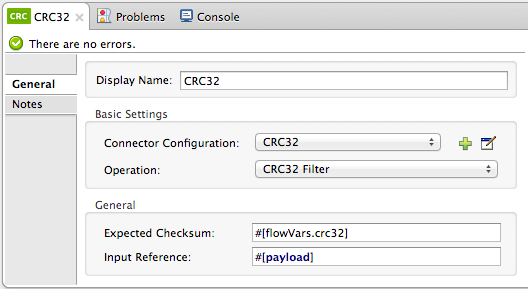
Attribute Req’d Value Display Name
x
A unique name for your message processor.
Connector Configuration
x
Create a "blank" global element satisfies Anypoint Studio’s configuration requirements and needs no further configuration.
-
Click the
 icon next to the Connector Configuration field.
icon next to the Connector Configuration field. -
Delete the default text in the Target Expression field, leaving this field blank, then click OK.
Operation
x
CRC32 Filter
Expected Checksum
x
Enter the Expected Checksum, matching the contents of the Target Expression field in the CRC32 global element in your configuration of the CRC32 calculation.
Input Reference
By default, Mule calculates based on the entire payload. Use the Input Reference field to specify a different target for the calculation, if necessary.
-
Configuring a CRC32 Message Processor with XML Editor or Standalone
-
Not required in Standalone: Create a "blank"
crc32:configglobal element, as per the code below, to satisfy Anypoint Studio’s configuration requirements.<crc32:config name="CRC32" doc:name="CRC32"/> -
Insert a
crc32:filterprocessor into your Mule flow, positioned at the point where you would like to verify the checksum. -
Configure the message processor’s attributes according to the table below.
<crc32:filter config-ref="CRC32" expectedChecksum="#[flowVars.crc32]" doc:name="CRC32 Filter"/>Attribute Req’d Value config-ref
x
Use the global element you created above.
doc:name
x
A display name for the element in Studio’s Visual Editor. Not applicable for Standalone.
expectedChecksum
x
Enter the Expected Checksum, matching the contents of the Target Expression field in the CRC32 global element in your configuration of the CRC32 calculation.
input-ref
By default, Mule calculates based on the entire payload. Use the Input Reference field to specify a different target for the calculation, if necessary.



