Expression Transformer Reference
| Mule Runtime Engine versions 3.5, 3.6, and 3.7 reached End of Life on or before January 25, 2020. For more information, contact your Customer Success Manager to determine how you can migrate to the latest Mule version. |
The Expression Transformer executes one or more expressions on the current message. The results of these expressions becomes the payload of the current message.
Minimum Configuration: An expression evaluator and the expression itself.
Discussion: An Expression Transformer evaluates one or more expressions on the current message. Each evaluated expression equates to a parameter in the returned message. However, if the returned message encompasses more than one expression, then the results of those expressions are an Object array.
The Expression Transformer has the same advanced properties as all other transformers with the addition of an optional list of return arguments.
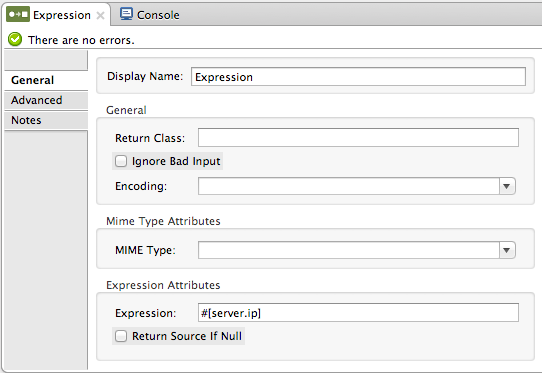
Click the General tab to specify an expression and an expression evaluator in the Expression attributes section.

You can select the expression evaluator from the pull-down list, or enter your own custom evaluator value. The expression evaluators in the pull-down list are already registered. If you set Evaluator to custom, you also need to specify the custom evaluator. In addition, when using a custom expression evaluator, you must first have registered the custom evaluator with the ExpressionEvaluatorManager. Note that the syntax of expressions you use vary depending on the evaluator.
The default value in the Expression field is #[]. You need to type a valid expression within the square brackets. For syntax details see the Mule Expression Language MEL documentation.
Check the Return source if Null box if you want the message payload source to be returned without modification when all expressions evaluate to null.
Use the Advanced tab to optionally configure the return arguments.
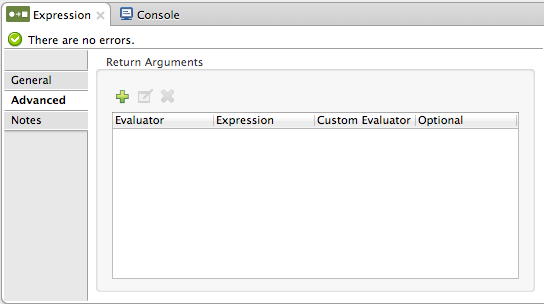
For each return argument, you enter or select from the pull-down list its expression evaluator. Then enter the expression to use. If you set Evaluator to custom, you also need to specify the custom evaluator. If you are using a custom expression evaluator, you must first have registered the custom evaluator with the ExpressionEvaluatorManager. Expression syntax varies depending on the evaluator.
When you have multiple expressions for return arguments, by default expression evaluation returns an error and stops when an expression evaluates to null. Check the Optional box if you want expression evaluation to continue to the next expression when an expression evaluates to null.



