<mule>
<spring:beans>
<spring:bean id = "customSerializer" class = "com.my.CustomSerializer" />
</spring:beans>
<configuration defaultObjectSerializer-ref = "customSerializer" />
</mule>Improving Performance with the Kryo Serializer
| Mule Runtime Engine versions 3.5, 3.6, and 3.7 reached End of Life on or before January 25, 2020. For more information, contact your Customer Success Manager to determine how you can migrate to the latest Mule version. |
The Kryo serializer and the Community Edition Serialization API let you serialize or deserialize objects into a byte array. These serializers decouple Mule and its extensions from the actual serialization mechanism, thus enabling configuration of the mechanism to use or the creation of a custom serializer. The Kryo serializer replaces plain old Java serialization, in which Java classes implemented java.io.Serializable or java.io.Externalizable to store objects in files, or to replicate classes through a Mule cluster.
Mule relies on serialization when applications read from or write to persistent object stores, a VM or JMS queue, or to an object from a file. Serialization also occurs when an distributes through a Mule cluster. The use of Kryo and Community Edition serializers greatly improves functionality and performance. Changing the serialization mechanism for each task can greatly improve functionality and performance.
You can develop projects with the Kryo and Community Edition serializers to:
-
Create a custom serializer using the Serialization API (CE)
-
Configure the Kryo Serializer (EE only)
Using the Serialization API
Community Edition - The open source Serialization API available in GitHub in the ObjectSerializer.java interface lets you serialize or deserialize objects into a byte array.
The Serialization API:
-
Is thread safe
-
Passes an OutputStream when serializing and streaming
-
Allows an InputStream as an input source
-
You can specify which classloader to use (the default is the current classloader)
-
When deserializing, if the obtained object implements the
DeserializationPostInitialisableinterface, the serializer is responsible for properly initializing the object before returning it
Configuring the Custom Serializer
Each application is able to configure the ObjectSerializer to use using the Mule <configuration> tag:
If no defaultObjectSerializer is configured, then a default implementation uses plain old Java serialization. This means that from a user perspective, there’s no behavioral change unless you specifically set a different serializer.
Note: The only component behavior that’s not affected by this component is the batch module, which for its own functionality reasons needs to work using the Kryo no matter what.
Obtaining a Configured ObjectSerializer
There are many ways to obtain an ObjectSerializer. Recommended approach is through dependency injection. The following shows how to get the ObjectSerializer that has been configured as the default:
public class MyClass {
@Inject
@DefaultObjectSerializer
private ObjectSerializer objectSerializer;
}Instead, if you want a specific named serializer (whether it’s the default or not) you can also do it like this:
public class MyClass {
@Inject
@Named ("mySerializer")
private ObjectSerializer objectSerializer;
}Finally, you can always pull it from the muleContext, although dependency injection is preferred:
// Returns the default object serializer
muleContext.getObjectSerializer();
// Returns a named object serializer
muleContext.getRegistry().get("mySerializer");Configuring the Kryo Serializer
Enterprise Edition - Mule provides the implementation of ObjectSerializer which relies on the Kryo framework. Using Kryo provides:
-
Better performance. Kryo is much faster than Java serialization
-
Support for a wider range on Java types. Kryo is not bounded by most of the limitations that Java serialization imposes like requiring to implement the Serializable interface, having a default constructor, etc
-
Support for compression: You can use either Deflate or GZip compression algorithms
The Kryo namespace configures this serializer:
<mule>
<kryo:serializer name = "kryo" />
<configuration defaultObjectSerializer-ref = "kryo" />
</mule>The configuration sets the default serializer to a Kryo based one. Additionally, you can also configure compression as:
<kryo:serializer name = "noCompression" compressionMode = "NONE" />
<kryo:serializer name = "deflate" compressionMode = "DEFLATE" />
<kryo:serializer name = "gzip" compressionMode = "GZIP" />Performance Using Kryo
Using Kryo provides performance improvements using these components:
-
Persistent or clustered object stores
-
Persistent or distributed VM queues
-
JMS transport
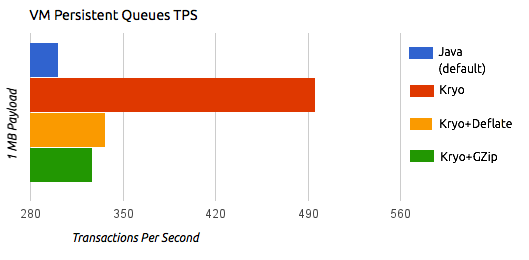
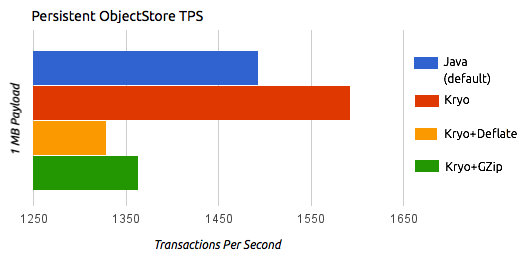
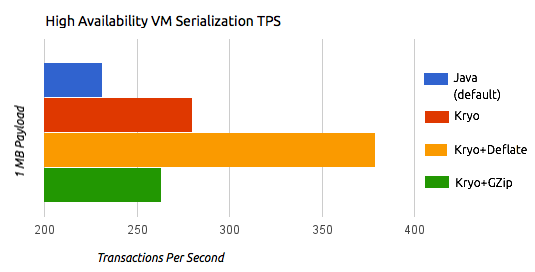
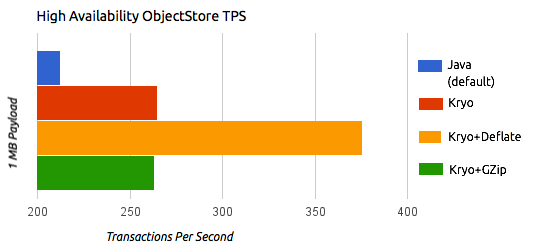
The following illustrations by the performance team at MuleSoft compare the transactions per second (TPS) of persistent and distributed VM queues and ObjectStore using the standard Java serializer and different Kryo settings.
Compression
The previous charts indicate that Kryo without compression is significantly faster than the standard serializer in all cases. However, the compression mode only provides an actual improvement on the high availability (HA) cases.
For the compression to be worthy, the amount of time the CPU spends compressing and decompressing has to be significantly lower than the amount of I/O time saved by reducing the payload size. Because network operations are typically slower than disk operations and because HA clustering requires node replication, which translates to more traffic), only in the HA case the compression paid off.
This is not a universal constant. You might be running Mule on machines with slower disks or higher I/O demands in which compression might be worthy on any case. Also, these tests were performed with 1 MB payloads, but the larger the data stream, the more worthy becomes the compression.
Performance Summary
The following are the performance results:
| Test | VM Persistent | OS Persistent | VM HA | OS HA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Kryo |
64.71% |
6.64% |
21.09% |
24.79% |
Kryo + Deflate |
11.84% |
-11.01% |
63.77% |
77.13% |
Kryo + GZip |
8.53% |
-8.69% |
13.93% |
23.96% |
The conclusions from table are that:
-
You can get up to a 77.13% improvement in performance when using distributed ObjectStores, 63.77% when using distributed VM queues and 64.71% when using local persistent VM queues.
-
Although local object stores don’t show much improvement. They are actually slower when using compression. There’s no use case in which you don’t get some level of gain when using Kryo.
Performance results are a guideline rather than an absolute fact. Depending on your application, environment, payload size, etc., the actual output may vary.
Limitations and Considerations
The following sections provide information you need to use serializers.
Changing Serializers Requires a Clean Slate
Serializers are not interoperable nor interchangeable. That means that if you decide to change the serializer your application uses, you need to make sure that all messages in VM and JMS queues have been consumed and that those queues are empty by the time the new serializer kicks in. This is because Kryo serializer won’t be able to read datagrams written by the Java searializer and vice-versa. The same thing applies to persistent ObjectStores. If you try to read an entry generated with a different serializer, you are out of luck.
Serialization in a Shared VM Connector
Mule treats domains as a way to share resources between applications, such as defining a VM connector on a domain to allow inter-app communication through VM message queues. However, serializers can only be configured at an application level, they cannot be configured at a domain. So what happens if applications A and B communicate with each other through a VM connector defined on a domain to which both belong, but A serializes using Java and B using Kryo? The answer is: it just works. Whenever either app tries to write to an endpoint which uses the shared connector, that particular message is not serialized with the application’s serializer but the one the VM connector is using. So this is good right? Yes, it’s good from the point of view of the plug and play experience. But notice that you won’t be able to tell that shared VM connector to use Kryo and get a performance improvement out of it.
Less Improvement for a Local Persistent ObjectStore
Unlike the other cases, the local persistent ObjectStore doesn’t show much improvement because of high contention on the ObjectStore implementation which pretty much absorbs all the gain.
No JMS Improvement Chart
Per the JMS API, the queues don’t work with raw payload objects. Instead, you have to provide an instance of the javax.jms.Message class. The broker client is then responsible for serializing it, not Mule. Therefore, the impact of Kryo in such an scenario is minimum. The only performance gain of using Kryo with JMS is that Mule serializes the MuleSession and puts it as a header in Base64 format. Serializing the MuleSession with Kryo can give you up to 10% performance speed, but we don’t consider it as an example use case since the big part of the serialization is up to the JMS broker instead of Mule.
Problematic Types
Although Kryo is capable is serializing objects that don’t implement the Serializable interface, setting Kryo as the default serializer doesn’t mean that components such as the VM transport, ObjectSerializer, or Cluster are able to handle objects which don’t implement such an interface. That’s because even though Kryo can deal with those objects, the Java APIs for those components still expect instances of Serializable in their method signatures.
Note: Standard serialization fails with an object that implements the Serializable interface. However if serialization contains another object which doesn’t implement the Serializable interface, Kryo is likely (but not guaranteed) to succeed. A typical case is a POJO containing an org.apache.xerces.jaxp.datatype.XMLGregorianCalendarImpl, which is in use in the NetSuite or Microsoft Dynamics CRM connectors.



