XSLT Transformer Reference
| Mule Runtime Engine versions 3.5, 3.6, and 3.7 reached End of Life on or before January 25, 2020. For more information, contact your Customer Success Manager to determine how you can migrate to the latest Mule version. |
Overview
You can use the XSLT Transformer to transform XML data using XSLT.
A XSLT transformer, unless configured otherwise, transforms XML data based on the default XSL template file.
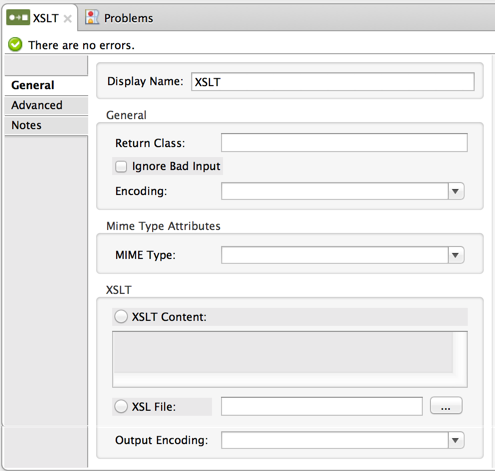
General Tab
Use the General tab to specify the return class, encoding, MIME type, and XSL transformation code.
You can specify a different XSL template file. You can browse to this file or enter the full path to the file. Rather than specifying a XSL file, you can type in the XSL content directly in the XSLT Content box. Either way that you specify the XSLT, you can also select the Output Encoding, such as the ISO Unicode or language formats, for the content output from the XML.

Advanced Tab
Use the Advanced tab to optionally configure additional properties.
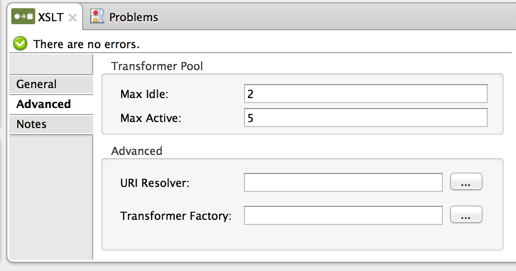
Transformer Pool: You can set Max Idle and Max Active values for the transformers pool. Because XSL transformation is expensive, and because Mule pools transformers for better throughput, you may want to set limits on the transformer pool when using XSLT transformers. Use Max Idle to set the maximum number of transformer instances that remain idle in the pool. Use Max Active to set the maximum number of XSLT transformers that are pooled at any given time. The default value for Max Idle is 2 and the default value for Max Active is 5.
URI Resolver: Change how the XSL output is validated. If not set, Mule uses a default resolver that checks for resources on the local file system and classpath.
Transformer Factory: If set, this is the fully qualified class name of the javax.xml.TransformerFactory instance to use. If not specified, Mule uses the default JDK factory TransformerFactory.newInstance().



