Anypoint Service Mesh 1.0
Anypoint Service Mesh enables you to extend your microservices network by including your non-MuleSoft applications into the Anypoint Platform sphere. You can then manage and secure your application network, including your non-Mule applications, seamlessly from a single pane.
Your non-MuleSoft microservices might be written using different languages and platforms, or might be deployed in different environments. To alleviate issues arising from differences in these microservices, Anypoint Service Mesh ensures the following application management advantages:
-
Provides resilient service-to-service communication using zero-trust policies to handle traffic control, fault tolerance and load balancing
-
Extends MuleSoft API Management capabilities to any non-Mule service, with policies, security and analytics all applied directly from Anypoint Platform
-
Amplifies reuse of services with discovery of non-Mule services within Exchange, available for use in future projects
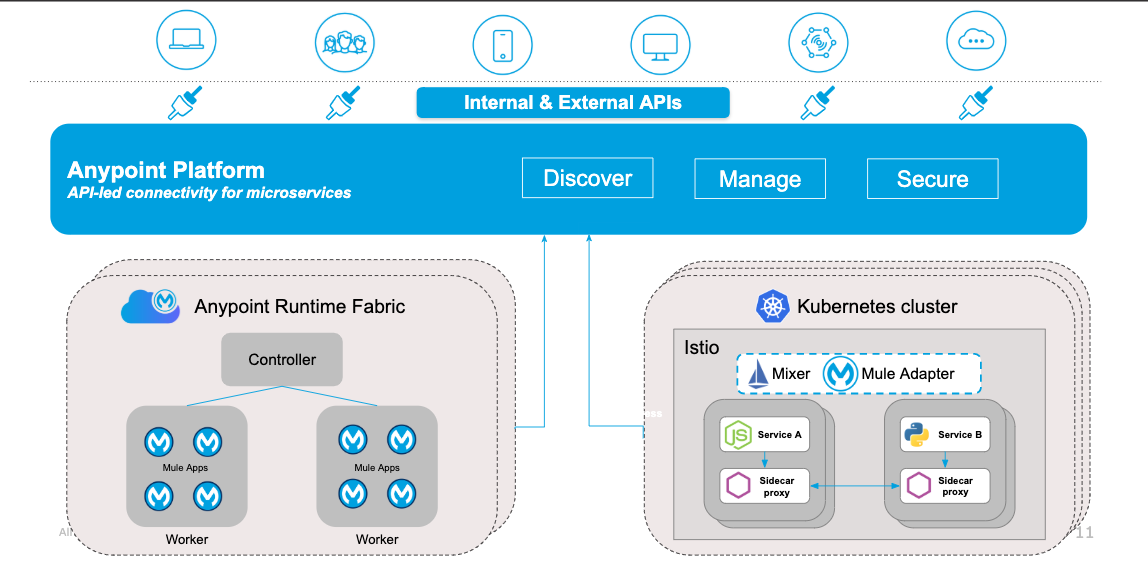
Anypoint Service Mesh Architecture
A service mesh is an independent architecture layer, which is encapsulated in a Kubernetes Cluster. In a service mesh architecture, instead of the services directly communicating with one another, a sidecar proxy is used to perform the same job.
The sidecar proxy enables you to bring your existing non-Mule microservices from the Kubernetes Cluster as APIs into Anypoint Platform. You can then manage these APIs within API Designer, API Manager, and Exchange. Additionally, you can monitor the health of your APIs using API analytics.
A mixer, whose key function is to provide a layer of abstraction over the different policy and telemetry backend systems, governs the sidecar proxies. Because of this abstraction, applications such as Anypoint Platform, enable the rest of Istio to be agnostic of the backend processing.
The mixer is architected on a general-purpose plug-in model, which provides flexibility in dealing with different infrastructure backend applications. These plug-in applications, known as adapters, enable the mixer to interface with the backend applications that deliver core functionality, such as logging, monitoring, enforcing quotas, performing ACL checks, and so on.

As illustrated in the diagram, at the top of the architecture is Anypoint Platform, which brings complete lifecycle API management capabilities to the microservices built with Mule runtime engine (Mule). These Mule instances might be deployed within CloudHub, or Runtime Fabric at your location.
Istio, which is installed on a Kubernetes Cluster, uses Envoy to manage the services using a sidecar proxy. The sidecar is responsible for any communication with the service, and resides within the same container as your service. With Anypoint Service Mesh enabled, you can continue to use Istio’s native policies for traffic control and security. These policies help ensure reliable and secure service-to-service communication.
The MuleSoft adapter and broker, which reside within the Istio mixer, connect components to Anypoint Platform. The adapter and broker enable sharing of metadata about all the services that are managed by the mesh. This allows for discovery of your existing microservices from the Kubernetes Cluster as APIs into Anypoint Platform.
After the services are discovered, Anypoint Exchange uses the metadata to automatically discover and create HTTP APIs for each service. These APIs can then be managed within API Manager. Similarly, Anypoint Monitoring uses the metadata to get information from the sidecar proxy and makes it available for API Analytics.
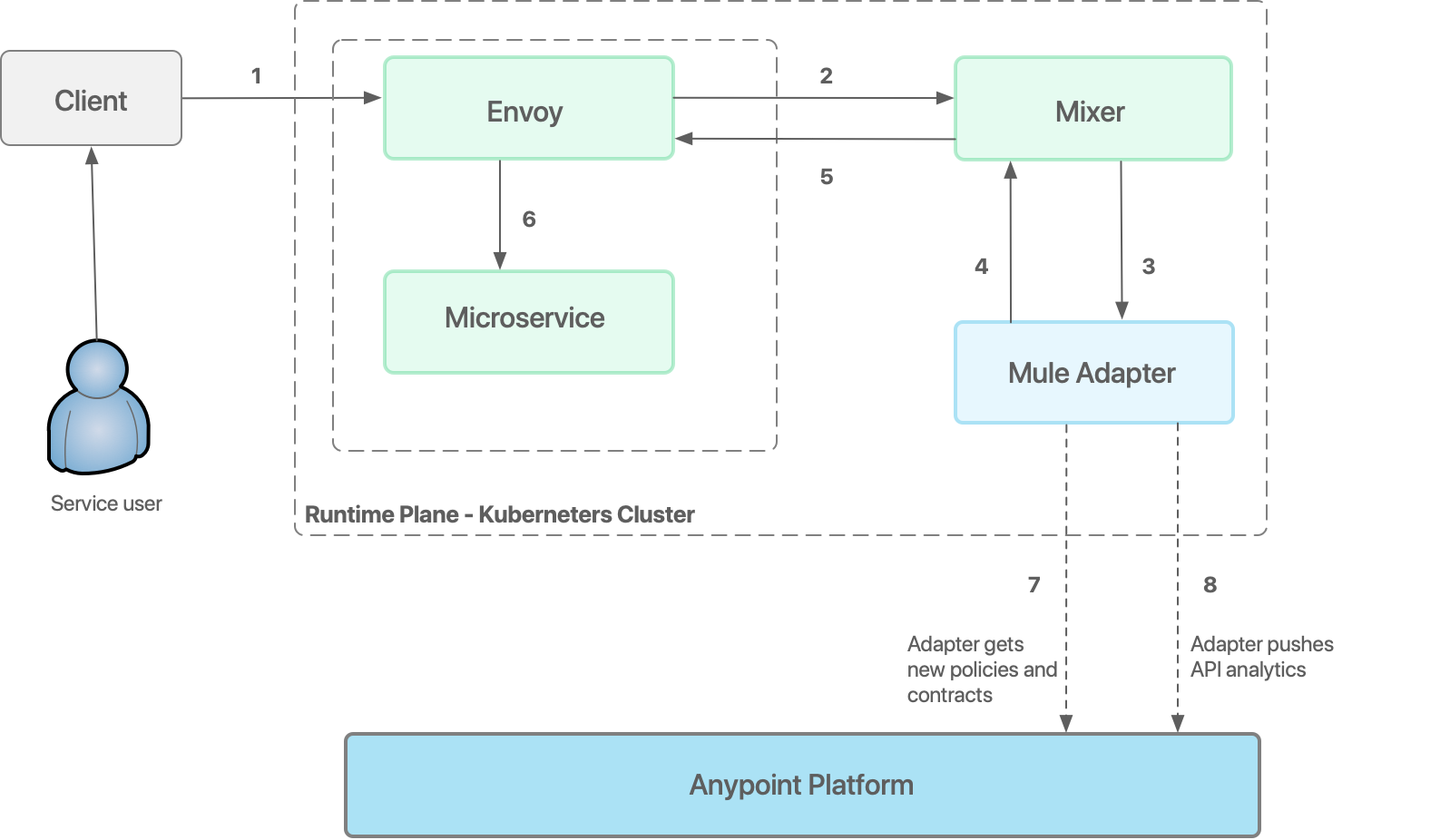
Service Request Flow
When a service is called, Anypoint Service Mesh ensures a smooth request flow and security checks as shown in the following diagram:
-
The client, which might be another microservice or any Kubernetes Ingress component, sends a request to the service.
-
Envoy captures the request and redirects it to the Istio-mixer.
-
The mixer adapter then calls the Anypoint Service Mesh adapter to perform policy checks and verifications.
-
The Anypoint Service Mesh adapter performs policy checks and responds back to the mixer.
-
The mixer communicates the outcome of the policy checks to the Envoy proxy.
-
When no policy violations are encountered, the request is routed to the microservice. The microservice runs the service logic and sends the response back to the client.
-
The adapter communicates with Anypoint Platform asynchronously to get the latest policies and contracts.
-
Finally, the adapter sends back the API analytics information to Anypoint Platform.