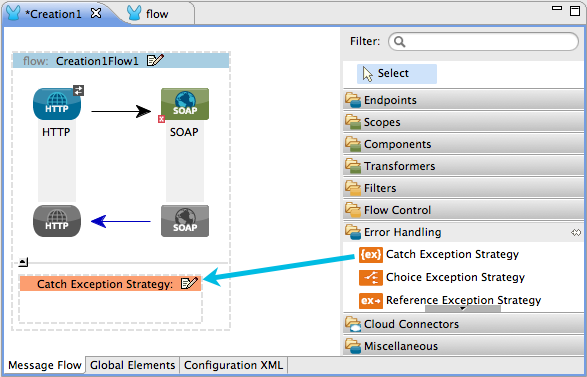
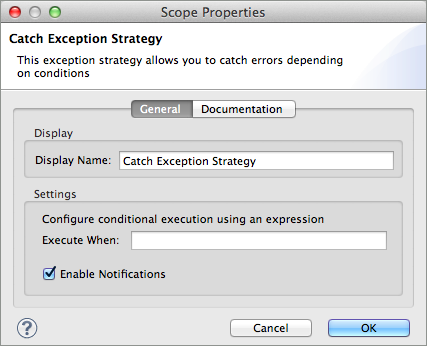
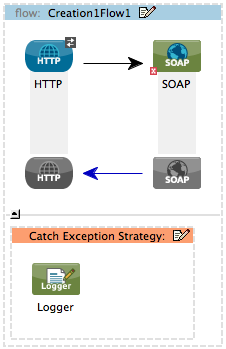
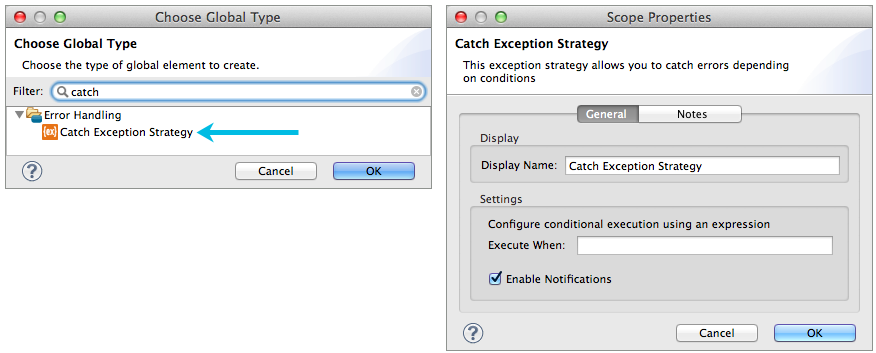
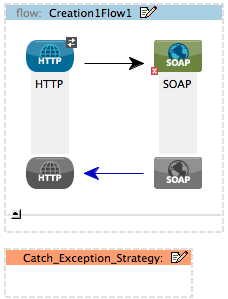
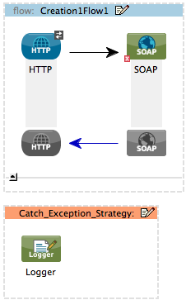
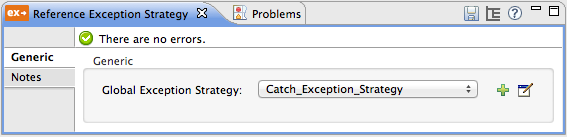
Use a catch exception strategy to design a unique strategy for handling a message that contains an error. Further, you can use a catch exception strategy to:
-
Avoid propagating exceptions to inbound endpoints
-
Avoid propagating exceptions to parent flows via Flow Reference Components
-
Ensure that a transaction processed by the flow will not be rolled back when an error occurs (i.e. The transaction is never “rolled back” to reattempt processing; Mule commits the transaction.)
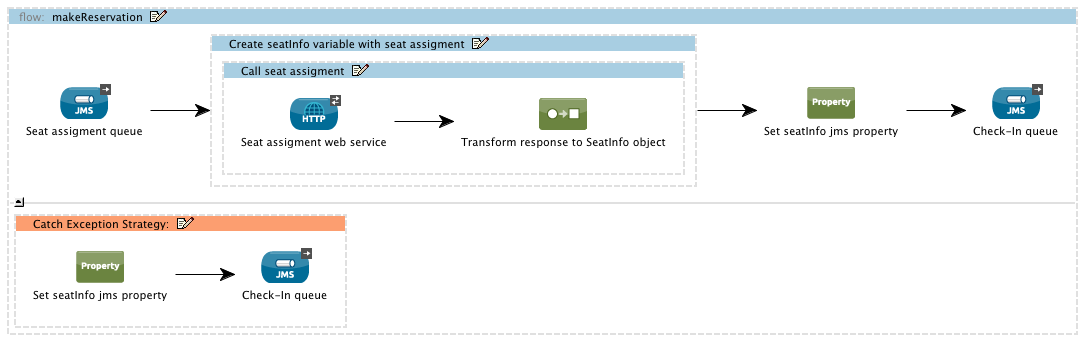
For example, suppose you have a flow that processes messages from a JMS queue (a reservation for a flight), enriches them by adding a property acquired from an external resource (seat assignment), and then sends them to another queue. You configure a catch exception strategy to handle errors that occur in this flow; when an error occurs during processing — say the seat information is not available from the external resource — the message throws an exception. The catch exception strategy catches the exception, applies a header to it to advise that “no seats are available,” and pushes the message out of the flow to its next designated queue.
Studio Visual Editor
Studio XML Editor or Standalone
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<mule xmlns="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core" xmlns:http="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http"
xmlns:jms="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/jms" xmlns:doc="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/documentation"
xmlns:spring="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:core="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core"
xmlns:json="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/json" xmlns:vm="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/vm"
xmlns:scripting="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/scripting" xmlns:ee="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/ee/core"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" version="EE-3.3.0" xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/http/current/mule-http.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/jms http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/jms/current/mule-jms.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-current.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/core/current/mule.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/json http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/json/current/mule-json.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/vm http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/vm/current/mule-vm.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/scripting http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/scripting/current/mule-scripting.xsd
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/ee/core http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/ee/core/current/mule-ee.xsd ">
<jms:activemq-connector name="Active_MQ" brokerURL="tcp://localhost:61616"
validateConnections="true" doc:name="Active MQ"/>
<flow name="makeReservation" doc:name="makeReservation">
<jms:inbound-endpoint queue="seatAssigment" connector-ref="Active_MQ" doc:name="Seat assigment queue"/>
<enricher target="#[flowVars['seatInfo']]" doc:name="Create seatInfo variable with seat assigment">
<core:processor-chain doc:name="Call seat assigment">
<http:outbound-endpoint host="localhost" port="1234" path="seatService"
doc:name="Seat assigment web service"/>
<http:http-response-to-object-transformer doc:name="Transform response to SeatInfo object"/>
</core:processor-chain>
</enricher>
<set-property propertyName="seatInfo" value="#[flowVars['seatInfo'].getSeatNumber()]"
doc:name="Set seatInfo jms property"/>
<jms:outbound-endpoint queue="checkin" connector-ref="Active_MQ" doc:name="Check-In queue"/>
<catch-exception-strategy doc:name="Catch Exception Strategy">
<set-property propertyName="seatInfo" value="No seat info available" doc:name="Set seatInfo jms property"/>
<jms:outbound-endpoint queue="checkin" connector-ref="Active_MQ" doc:name="Check-In queue"/>
</catch-exception-strategy>
</flow>
</mule>