#[exception.causedBy(ExceptionType)]Checks that the exception is an instance of ExceptionType
You can define a choice exception strategy to customize the way Mule handles a message with an error based on the message’s content at the moment it throws an exception. A choice exception strategy catches all exceptions thrown within its parent flow, examines message contents and exception type, then routes messages to the appropriate exception strategy for processing.
Usually, you define more than one exception strategy within a choice exception strategy. Each exception strategy - either catch or rollback - uses a Mule expression to advise the choice exception strategy which type of messages it accepts and processes.
Here’s how it works: when the choice exception strategy catches an exception, it evaluates the type of exception and the message contents at the time the error occurred. Then it checks the expression attribute of each of its exception strategies one by one, serially, to see which one of them should handle the error. It then routes the message to the first exception strategy that evaluates to true (has a expression that matches the expression of the message). If none of its exceptions strategies can handle the error, the choice exception strategy routes the message to Mule’s default exception stategy.
You can put any number of catch or rollback exception strategies into a choice exception strategy.
You cannot put a choice exception strategy inside another choice exception strategy
You can use any Mule expression evaluator as the expression attribute of an exception strategy. Consider using an exception-type expression evaluator, such as org.mule.example.ValidationException, when you need to route messages based on the type of exception they throw.
Use a choice exception strategy to enable Mule to make decisions about how to handle each error that occurs in a flow.
For example, in a flow that processes orders, you can use a choice exception strategy to apply the following error handling rules:
Messages that throw an AlreadyProcessedException should be discarded.
Messages that throw a ValidationException should be sent to an invalid order queue.
All other messages which throw exceptions should be rolled back to retry processing.
A choice exception strategy can evaluate the exception type of each message that throws an exception in this flow and route them to one of three exception strategies:
a catch exception strategy to process and discard all AlreadyProcessedExceptions
a second catch exception strategy to process all ValidationExceptions and send them to an invalid orders queue
a rollback exception strategy to roll back the order transaction in order to retry processing in the parent flow
The following lists some useful expressions which check for specific exceptions:
| Expression and Operation | Example |
|---|---|
Checks that the exception is an instance of ExceptionType |
|
Check that the exception exactly matches the ExceptionType |
|
Checks that the exception type matches a particular regular expression (Regex) String |
|
From the Error Handling palette group, drag and drop the choice exception strategy icon into the footer bar of a flow.
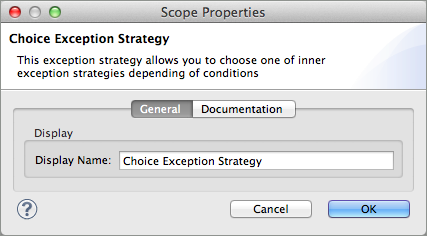
Double-click the title bar of the exception strategy to open its Properties panel, then enter a name for your choice exception strategy in the Display Name field.
From the Error Handling palette group, drag and drop one or more catch or rollback exception strategy icons into the choice exception strategy box.
| Keep in mind that the choice exception strategy checks the expression attribute of each of its exception strategies one by one, serially, to see which one of them should handle the error; it then routes the message to the first exception strategy that evaluates to true. Therefore, organizing your exception strategies keeping in mind that the top-most will be evaluated first, then the one below it, and so on. You cannot rearrange the exception strategies once they have been placed inside the choice exception strategy. |
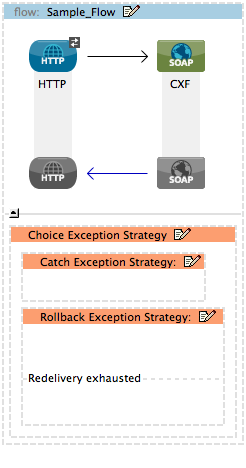
Follow the instructions to define and configure each catch exception strategy and rollback exception strategy. Be sure to enter a Mule expression in the Execute When or When fields of each catch or rollback (respectively) exception strategy that have you put into the choice exception strategy. The contents of the Execute When or When field determine what kind of errors the exception strategy accepts and processes.
| You can leave the Execute When field blank in the last exception strategy configured inside your choice exception strategy. An exception strategy with a blank Execute When field accepts and processes any and all kinds of exceptions that messages throw in the parent flow. |
Drag building blocks from the palette into each catch exception strategy and rollback exception strategy box to build flows that will process message with errors. Each catch and rollback exception strategy can contain any number of message processors.
In your flow, below all the message processor, add a choice-exception-strategy element. Refer to code below.
Configure attributes of the exception strategy according to the table below.
| Attribute | Req’d | Value |
|---|---|---|
doc:name |
x |
A unique name for the rollback exception strategy in your application. Not required in Standalone. |
<choice-exception-strategy doc:name="Choice Exception Strategy"/>As child elements, add one or more catch or rollback exception strategy icons to your choice exception strategy.
| Keep in mind that the choice exception strategy checks the expression attribute of each of its exception strategies one by one, serially, to see which one of them should handle the error; it then routes the message to the first exception strategy that evaluates to true. Therefore, organize your exception strategies keeping in mind that the top-most will be evaluated first, then the one below it, and so on. You cannot rearrange the exception strategies once they have been placed inside the choice exception strategy. |
<flow name="Sample_Flow">
...
<choice-exception-strategy doc:name="Choice Exception Strategy">
<catch-exception-strategy doc:name="Catch Exception Strategy"/>
<rollback-exception-strategy doc:name="Rollback Exception Strategy"/>
</choice-exception-strategy>
</flow>Follow the instructions to define and configure each catch exception strategy and rollback exception strategy. Be sure to define a Mule expression as the value of the when attribute of each catch or rollback (respectively) exception strategy that you have put into the choice exception strategy. The value of the when attributes determine what kind of errors the exception strategy accepts and processes.
You can leave the value of the when attribute empty in the last exception strategy configured inside your choice exception strategy. An exception strategy with an empty when attribute accepts and processes any and all kinds of exceptions that messages throw in the parent flow.
|
Add message processor as child elements in each catch exception strategy and rollback exception strategy to build exception strategy flows that will process messages with errors. Each catch and rollback and exception strategy can contain any number of message processors.
You can create one or more global exception strategies to reuse in flows throughout your entire Mule application. First, create a global choice exception strategy, then add a Reference Exception Strategy to a flow to apply the error handling behavior of your new global choice exception strategy.
In the Global Elements tab, create a Choice Exception Strategy.
Define a name for your global exception strategy, then click OK to save.
Click the Message Flow tab below the canvas. On the Message Flow canvas, note that your newly created global choice exception strategy box appears outside the parent flow. Because it is global, your new rollback exception strategy exists independently of any Mule flow.
Follow steps 3 - 5 above to configure exception strategies within your choice exception strategy, then define the flows to handle errors when they occur.
Above all the flows in your application, create a choice-exception-strategy element.
Configure attributes of the exception strategy according to the table below.
| Attribute | Req’d | Value |
|---|---|---|
doc:name |
x |
A unique name for the rollback exception strategy in your application. Not required in Standalone. |
Follow steps 3 - 5 above to configure exception strategies within your choice exception strategy, then define the flows to handle errors when they occur.
Use a reference exception strategy to instruct a flow to employ the error handling behavior defined by your global choice exception strategy. In other words, you must ask your flow to refer to the global catch exception strategy for instructions on how to handle errors.
From the Error Handling palette group, drag and drop the Reference Exception Strategy icon into the footer bar of a flow.
Double-click to open the Reference Exception Strategy Patter Properties panel.
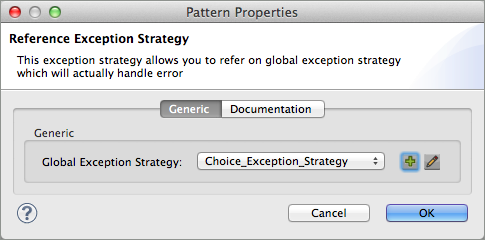
Use the drop-down to select your Global Exception Strategy.
Click OK to save your changes.
You can create a global rollback exception strategy (i.e. access the Choose Global Type panel) from the reference exception strategy’s pattern properties panel. Click the  button next to the Global Exception Strategy drop-down and follow the step above to create a global choice exception strategy. button next to the Global Exception Strategy drop-down and follow the step above to create a global choice exception strategy.
|
In your flow, below all the message processor, add a reference-exception-strategy element. Refer to code below.
Configure attributes of the exception strategy according to the table below.
| Attribute | Req’d | Value |
|---|---|---|
ref |
x |
The name of the global exception strategy to which your flow should refer to handle exceptions. |
doc:name |
x |
A unique name for the rollback exception strategy in your application. Not required in Standalone. |
<exception-strategy ref="Global_Choice_Exception_Strategy" doc:name="Reference Exception Strategy"/>| You can append a Reference Exception Strategy to any number of flows in your Mule application and instruct them to refer to any of the global catch, rollback or choice exception strategies you have created. You can direct any number of reference exception strategies to refer to the same global exception strategy. |
Learn how to configure catch exception strategies.
Learn how to configure rollback exception strategies.