HTTP Connector - Deprecated
| Mule Runtime Engine versions 3.5, 3.6, and 3.7 reached End of Life on or before January 25, 2020. For more information, contact your Customer Success Manager to determine how you can migrate to the latest Mule version. |
|
As of Mule 3.6 and later, the HTTP endpoint-based connector and transport has been replaced by an operation-based HTTP connector. The legacy endpoint-based connector will be removed in a future version. See HTTP Connector for more information about the HTTP operation-based connector and how to migrate your projects to it. |
Use the HTTP Connector to send and receive requests over HTTP transport protocol, or HTTPS over the SSL protocol. Configured as either inbound (also known as message sources) or outbound, HTTP endpoints use one of two message exchange patterns: request-response or one-way.
To learn more about endpoints, refer to Anypoint Connectors.
Configuration
Complete the following procedure to add an HTTP endpoint to a flow in your Mule application.
-
In Studio, drag the HTTP icon from the Studio palette to the canvas. Position the endpoint at the beginning of a flow to use it as an inbound endpoint (see image below). Position the endpoint anywhere else in the flow to use it as an outbound endpoint.
-
Double click the HTTP building block to open its properties editor.
-
Refer to the sub-sections below to configure the HTTP endpoint within the tabs in the properties editor.
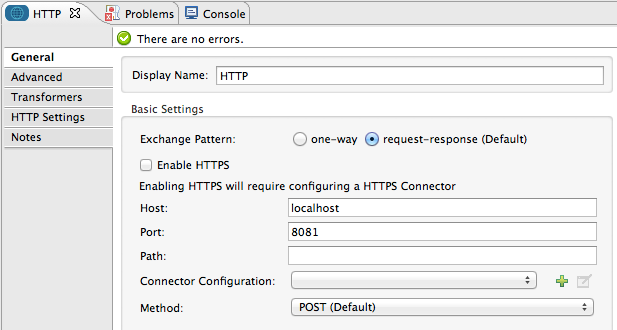
General Tab

| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Display Name |
Defaults to the generic endpoint name. Change the display name, which must be alpha-numeric, to reflect the endpoint’s specific role, i.e. |
Exchange Pattern |
Select whether the endpoint should be set to request-response or one-way. |
Enable HTTPS |
Check this box to send HTTPS over SSL protocol. If you enable HTTPS, ensure that you configure, then reference a global HTTPS connector on your endpoint. |
Host |
Enter the location of the host server to which the HTTP must connect. Enter the location as a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) or an IP address. Defaults to |
Port |
Enter a number to identify the port through which the HTTP endpoint must connect to the host server. Defaults to |
Path |
Specify the location in the host domain to which the HTTP must connect. |
Connector Configuration |
Use the dropdown list to select a previously created connector configuration for this endpoint. If you have not created a connector configuration for this type of endpoint, you can do so from this window by clicking Add. Click Edit to modify a previously created global element. |
Method |
(Applies to outbound endpoints only.) Select the HTTP method the connector should use. |
Advanced Tab
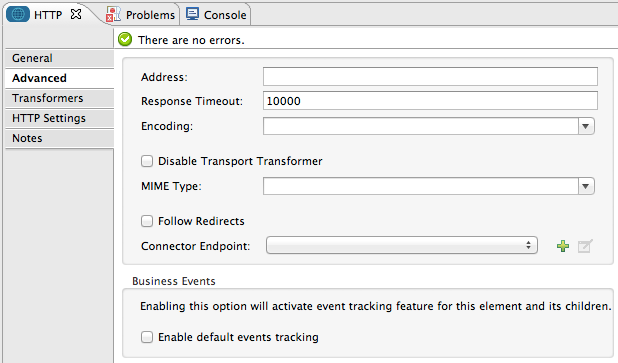
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
Address |
Enter the address for this endpoint, i.e. http://localhost:8081/path. |
Response Timeout |
Specify how long the endpoint must wait for a response (in ms). The default is 1000 ms. If set to 0, time out is disabled. |
Encoding |
Choose from a drop-down to identify the string encoding for a message (i.e. UTF-8). |
Disable Transport Transformer |
To facilitate processing, an HTTP endpoint in Mule automatically applies default transformations to messages it receives. These default transformations make the message contents more “Mule friendly. However, if you want the HTTP endpoint to strictly maintain the data format of messages it receives, check the Disable Transport Transformer box. |
MIME Type |
Select from the dropdown list one of the formats this endpoint supports. For example, set the MIME type to |
Follow Redirects |
(Applies to outbound endpoints only.) If a GET request encounters a redirectLocation header, setting this to true will forward the request to the redirect URL. This only works when using GET since you cannot automatically follow redirects when performing a POST. |
Connector Endpoint |
Use the dropdown list to select a previously configured global endpoint reference. If you have not created a global element for this type of endpoint, you can do so from this window by clicking Add. Click Edit to modify a previously created global element. |
Enable default events tracking |
Enable default business event tracking for this endpoint. |
|
Host and Path, or Address? If you enter the URI for the host server in the Address field, you don’t need to enter any information in the Host and Path fields. Similarly, if you entered host server information in the Host and Path fields, you don’t need to enter a URI in the Address field. Apply either the Host and Path attributes, OR the Address attribute to an HTTP endpoint. |
Transformers Tab
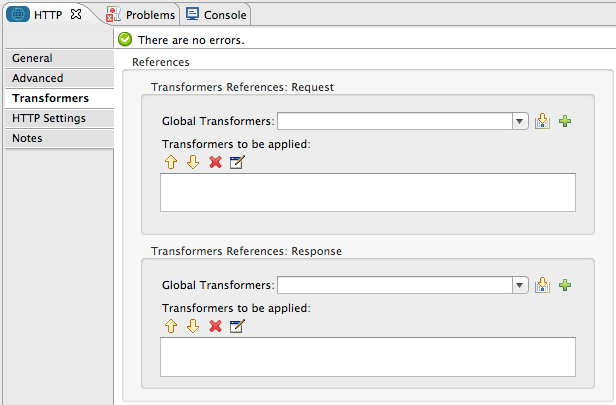
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
Request Transformer References |
Enter a list of synchronous transformers that will be applied to the request before it is sent to the transport. |
Response Transformer References |
Enter a list of synchronous transformers that will be applied to the response before it is returned from the transport. |
|
What is a Connector Configuration? Mule ESB uses Global Elements, like the HTTP/HTTP Connector Configuration and the HTTP Polling Connector Configuration, to set reusable configurations. Rather than repeatedly write the same code to apply the same configuration to multiple message processors, you can create one global element that details your configurations or transport details. Then, instruct any number of message processors in your Mule application to reference that global element. Global transport configurations do not exist within a Mule flow. Rather, the configurations reside in a global connector on the Global Elements tab on the Studio canvas, or at the top of the application in the XML configuration. An HTTP endpoint in a flow simply references a global connector to obtain transport configuration details. |
HTTP Settings Tab
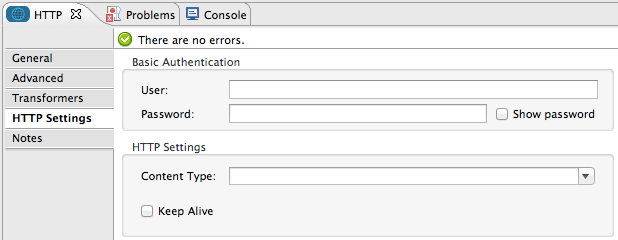
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
User |
Enter the username that the HTTP endpoint uses to identify itself to the host server. |
Password |
Enter the password that the HTTP endpoint uses to identify itself to the host server. |
Content Type |
Use the drop-down box to select the type of content the HTTP request or response contains. |
Keep Alive |
Check the Keep Alive box to maintain an open socket connection when a small interruption occurs. |
Reference Documentation
-
See the HTTP Transport Reference for details on setting the properties for an old HTTP endpoint using an XML editor.
-
See the HTTP Connector Reference for details on setting the properties for an new connector based HTTP endpoint using an XML editor.



