About Supported Network Topologies for Anypoint Private Cloud Edition
To ensure platform performance, stability, and high-availability, Anypoint Platform Private Cloud Edition supports two network topologies outlined in the sections below.
In both configurations, to ensure high availability and performance, each node must run on its own physical server. If you are using a virtual machine to host these nodes, you must ensure that each VM node is running on a separate physical server.
| Only VMWare bare metal virtualization environments and physical servers are supported. For information on using VMWare, see Creating a Virtual Machine using VMWare. |
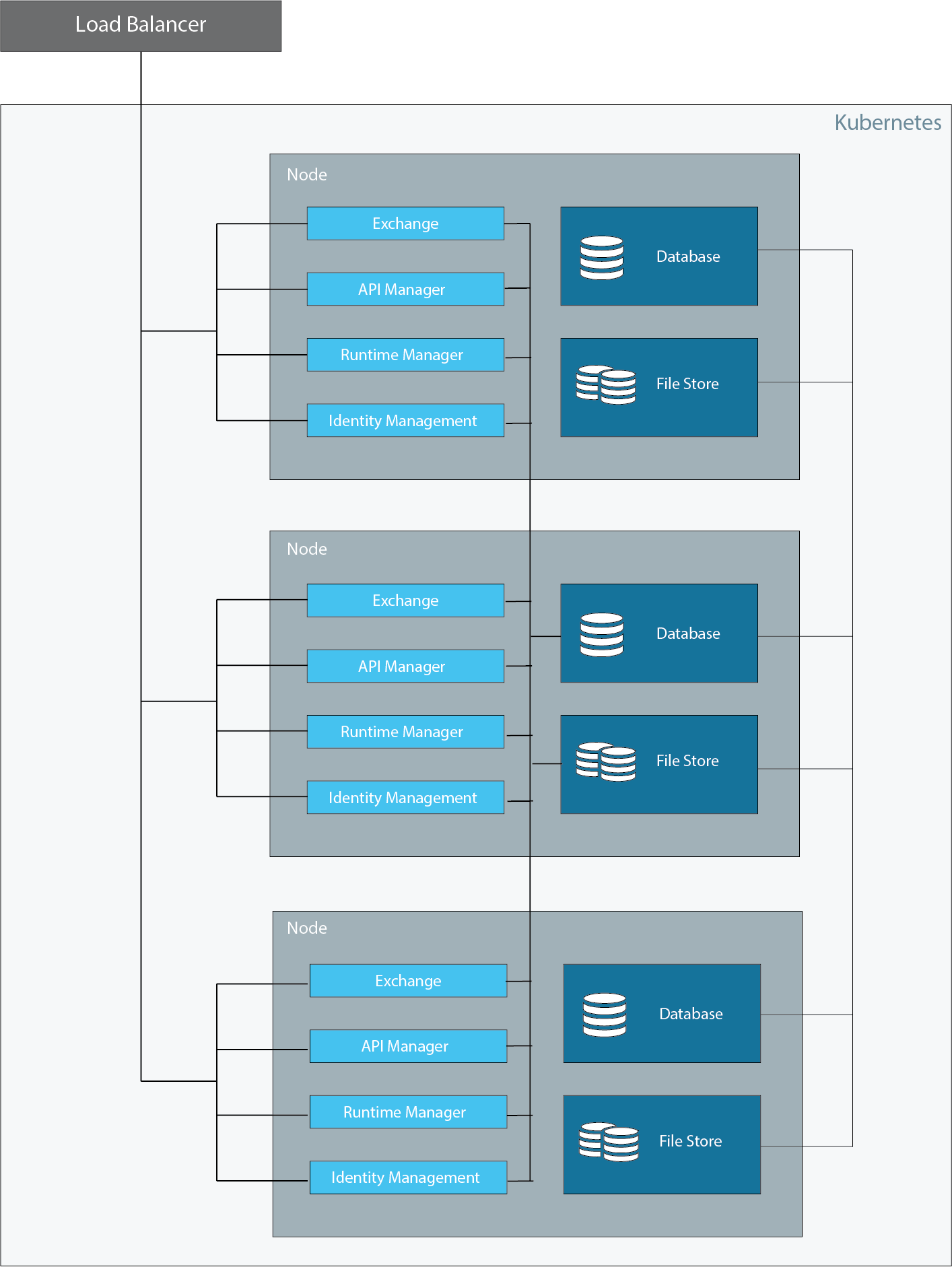
3-node Configuration
The minimum supported network topology for a production environment is a 3-node configuration as shown in the following diagram:

This configuration represents the minimum number of nodes that can enable high-availability and failover. In this configuration, each node hosts the platform applications and services. You must configure a load balancer to use round-robin distribution of traffic among each of the three nodes.
Each node also hosts an instance of the database and file store. Hosting the database and object store enables persistence, but requires larger minimum disk and memory requirements. Although each node contains a database, only one of the database is used as the master. Applications on each node write to this database only. The other two database instances are hot standby instances of the master database that take over as the master database in case of failure.
6-node Configuration
The maximum supported network topology is a 6-node configuration as shown in the following diagram:
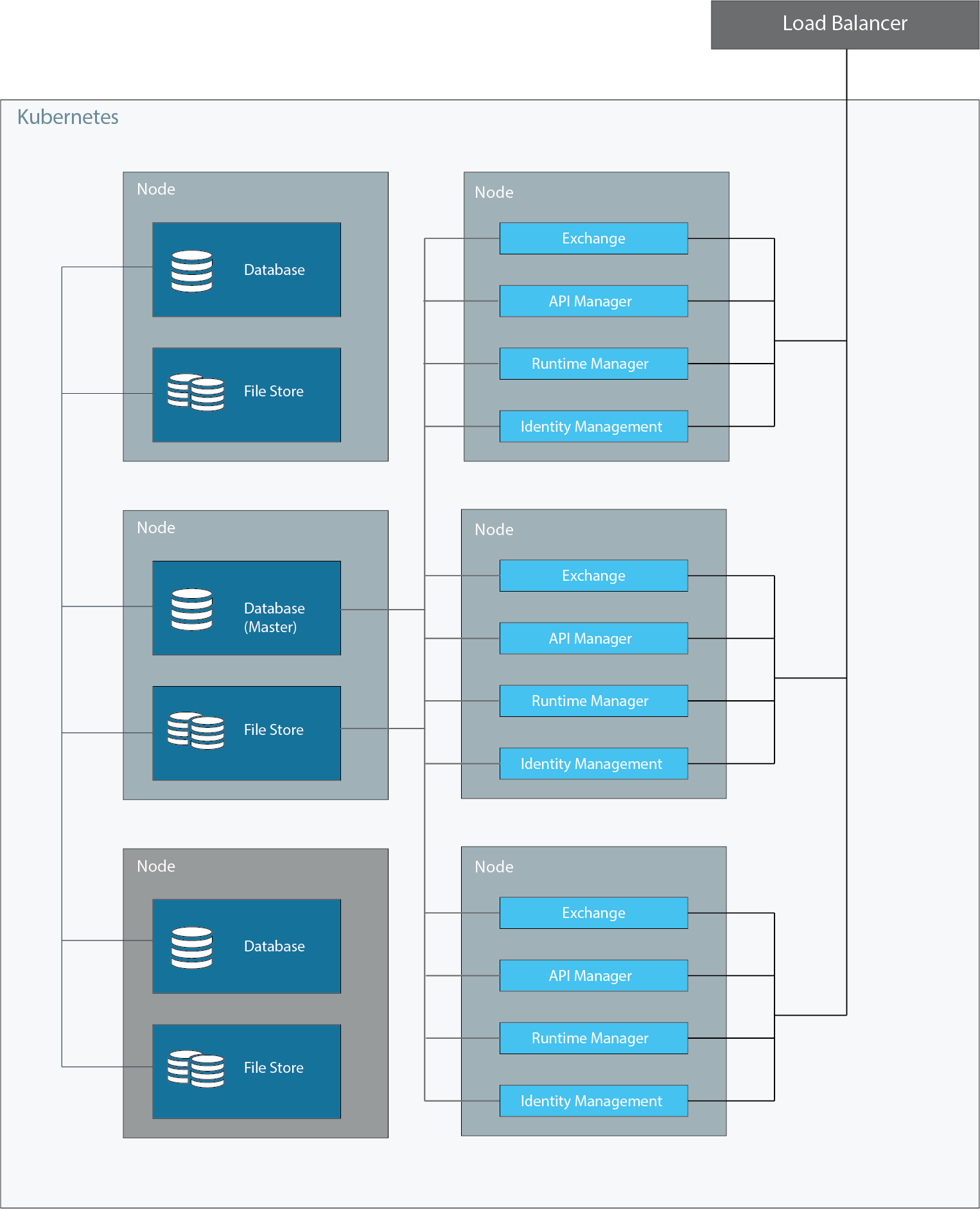
In this configuration, three nodes are dedicated to hosting the platform applications and services. The other three nodes host the database and file store instances. Although each node contains a database, only one of the database nodes is used as the master. Applications on each node write to this database only. The other two database instances are hot standby instances of the master database that take over as the master database in case of failure.
You must configure a load balancer to use round-robin distribution of traffic among all of the nodes in your cluster.



