-
Receives or sends messages to only one resource.
Transaction Management
| Mule Runtime Engine versions 3.5, 3.6, and 3.7 reached End of Life on or before January 25, 2020. For more information, contact your Customer Success Manager to determine how you can migrate to the latest Mule version. |
Overview
Mule applies the concept of transactions to operations in application for which the result cannot remain indeterminate. In other words, where a series of steps in a flow must succeed or fail as one unit, Mule uses a transaction to demarcate such a unit. For example, you might use a transaction to encapsulate several steps in a flow for which the end result involves committing information to a database. In this type of scenario, the commit is either entirely complete and succeeds, or is incomplete and it fails. Even if partially complete, the commit – or transaction – fails. Where a transaction fails, Mule rolls back the operations within the transaction so that no one part results in partial completion.
You can demarcate a transaction by applying a transaction to a connector. If a Mule flow begins with a transactional resource (such as an inbound connector), Mule can start a new transaction and manage the entire flow as a transaction. If your flow includes a transactional outbound connector, Mule manages the outgoing operation as a transaction. With both a transactional inbound and outbound connector, Mule executes the outgoing operation as part of the transaction initiated by the inbound connector.
The amount of global elements to which the transactional resource references determine the [Transaction Type]. Disregarding the resource type, you can only join multiple endpoints on a same transaction only if they all refer the same global element.
The following connectors support transactional demarcation:
-
JMS
-
JDBC
-
VM
Note: As of Mule 3.5.0, the Database Connector replaces the JDBC connector, and the JDBC connector is deprecated. Applications that use the JDBC transport continue to work with the 3.5.0 Enterprise Runtime, but the connector is no longer available in the Studio palette to add to applications.
A Mule flow may begin with a non-transactional inbound connector – such as HTTP or SFTP – but which requires the use of a transaction within the flow. For example, a Mule flow may accept information from an external Web service, then transform the data, before charging a credit card, and saving invoice information to a database. In such a situation, you can demarcate a transaction by wrapping the credit card charge and database commit operations within a transaction to ensure either complete success or complete failure and rollback.
Transaction Types
Mule supports three different types of transactions: single resource, multiple resource, and extended architecture (XA). The following table describes characteristics of each type.
Note: JDBC is deprecated.
| Type | Characteristics | Number of Resources | Available Resources | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
|
|
||
|
>1 |
|
|
|
|
>1 |
|
|
|
Multi-source vs. XA While XA Transactions offer similar functionality, Multiple Resource transactions use less overhead. XA transactions are more reliable. Both can include JDBC resources. |
Prerequisites
This document assumes that you are familiar with Mule ESB and/or the Anypoint Studio interface. You should also have some knowledge of transaction processing and be familiar with Anypoint Connectors.
Configuring Transactions
You can demarcate a transaction by either applying a transactional configuration to a connector, or by wrapping several elements in a transactional scope.
-
Apply a transaction to an inbound connector when you want Mule to handle the complete flow as a transaction.
-
Apply a transaction to an outbound connector when you want Mule to handle the outgoing operation as part of an existing transaction.
-
Apply a transaction as a wrapper (known as a scope in Studio) when you want to apply a transaction to elements within a flow that do not begin with a inbound connector configured as a transaction.
The following subsections outline the steps to apply transactions in your flow.
Applying a Transaction to a Connector
You can apply a transaction to any of the following inbound or outbound connectors:
-
JMS
-
VM
-
JDBC (Deprecated)
Studio Visual Editor
-
In the connector’s properties editor, click the General tab to access the Transaction pane (see image below of the JMS connector).
image::jms-transaction.png[jms_transaction] -
Configure the transactional attributes according to the tables below.
Attribute Value Available on Connector Use Type
JMS Transaction
JMS
Apply a transaction to a flow that involves a single resource (simple).
JDBC Transaction
JDBC
Apply a transaction to a flow that involves a single resource (simple).
VM Transaction
VM
Apply a transaction to a flow that involves a single resource (simple).
XA Transaction
JMS VM JDBC
Apply a transaction to a flow that involves multiple resources.
Client Ack Transaction
JMS
Apply a transaction to a flow that involves multiple resources.
Multi-resource Transaction
JMS VM JDBC
Apply a transaction to a flow that involves multiple resources.
Action
NONE
JMS VM JDBC
When it receives a message, Mule resolves the transaction, then executes the operation as non-transactional.
ALWAYS_BEGIN
JMS VM JDBC
When it receives a message, Mule always starts a new transaction.
BEGIN_OR_JOIN
JMS VM JDBC
When it receives a message, Mule joins a transaction if one is already in progress. Otherwise, Mule simply begins a new transaction.
ALWAYS_JOIN
JMS VM JDBC
When it receives a message, Mule always expects a transaction to be in progress, and always joins the transaction. If no transaction is in progress, Mule throws an exception.
JOIN_IF_POSSIBLE
JMS VM JDBC
Default When it receives a message, Mule joins the current transaction if one is available. Otherwise, Mule does not begin a transaction.
NOT_SUPPORTED
JMS VM JDBC
When it receives a message, this outbound connector executes outside the transactional operation; the transaction continues and does not fail.
Timeout
-
JMS VM JDBC
Insert an integer to represent the number of milliseconds (ms) that Mule allows to pass before it ends the transaction. Important: The timeout transaction is only taken into account in XA transactions.
-
If applying an XA transaction type to your connector, you have the option to check the Interact With External box. When checked, Mule acknowledges transactions that began externally. For example, if you set the transaction Action to BEGIN_OR_JOIN, and check Interact With External, Mule joins any transaction that is already in progress when it receives a message, regardless of whether the transaction began outside of Mule.
-
If you applied an XA transaction to multiple connectors in your flow, access the global connectors each references, and configure the connectors to use XA-enabled resources.
Use Transactions Configuration Reference for quick access to attribute configurations.
XML Editor
-
Add a
transactionalchild element to the inbound connector you wish to make transactional.Child Element
Available on Connector
Use
jms:transaction
JMS
Apply a transaction to a flow that involves a single resource (simple).
jdbc-ee:transaction
JDBC
Apply a transaction to a flow that involves a single resource (simple).
vm:transaction
VM
Apply a transaction to a flow which involves a single resource (simple).
xa-transaction
JMS VM JDBC
Apply a transaction to a flow that involves multiple resources.
jms:client-ack-transaction
JMS
Apply a transaction to a flow that involves multiple resources.
ee:multi-transaction
JMS
Apply a transaction to a flow that involves multiple resources.
-
Configure transactional attributes:
Attribute Value Available on Connector Use action
NONE
JMS VM JDBC
When it receives a message, Mule resolves the transaction, then executes the operation as non-transactional.
ALWAYS_BEGIN
JMS VM JDBC
When it receives a message, Mule always starts a new transaction. If a transaction already exists, Mule resolves the transaction.
BEGIN_OR_JOIN
JMS VM JDBC
When it receives a message, Mule joins a transaction if one is already in progress. Otherwise, Mule simply begins a new transaction.
ALWAYS_JOIN
JMS VM JDBC
When it receives a message, Mule always expects a transaction to be in progress, and always joins the transaction. If no transaction is in progress, Mule throws an exception.
JOIN_IF_POSSIBLE
JMS VM JDBC
When it receives a message, Mule joins the current transaction if one is available. Otherwise, Mule does not begin a transaction.
NOT_SUPPORTED
JMS VM JDBC
When it receives a message, this outbound connector executes outside the transactional operation; the transaction continues and does not fail.
timeout
-
JMS VM JDBC
Insert an integer to represent the number of milliseconds (ms) that Mule allows to pass before it ends the transaction. Important: The timeout transaction is only taken into account in XA transactions.
interactWithExternal
true
JMS VM JDBC
When set to true, Mule acknowledges transactions that began externally. For example, if you set the transaction action to BEGIN_OR_JOIN, and set interactWithExternal to true, Mule joins any transaction that is already in progress when it receives a message, regardless of whether the transaction began outside of Mule.
-
If you applied an XA transaction to multiple connectors in your flow, access the global connectors each references, and configure the connectors to use XA-enabled resources.
View Namespace
<mule xmlns:jms="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/jms"
...
xmlns:xsi="
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/jms
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/jms/current/mule-jms.xsd"><jms:inbound-endpoint doc:name="JMS">
<xa-transaction action="ALWAYS_BEGIN" timeout="35000"/>
</jms:inbound-endpoint>Use Transactions Configuration Reference for quick access to attribute configurations.
Applying a Transaction as a Scope
Studio Visual Editor
Enterprise
-
From the Scopes palette group, drag a Transactional scope onto the canvas. Drag building blocks into the Transactional scope to build your transaction.
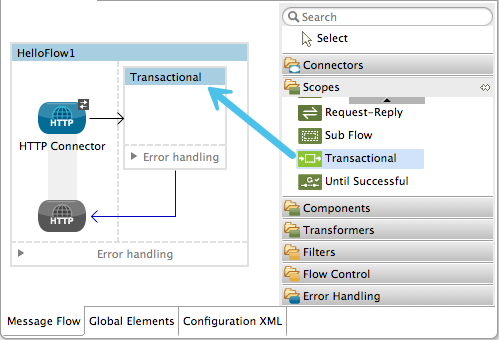
Alternatively, select multiple building blocks in a flow (shift+left click), then right-click to select Wrap in… > Transactional.
-
Configure the details of the transaction according to the table below.
Field Value Use Display Name
-
Provide a meaningful name for the transaction scope in your flow.
Type
Simple Transaction
_Default
_Apply a transaction to a flow that involves a single resource. See Single Resource Transaction for details.XA Transaction
Apply a transaction to a flow that involves multiple resources: JMS, VM or JDBC. See XA Transaction for details.
Multi Transaction
Apply a transaction to a flow that involves multiple resources: JMS or VM. See Multiple Resource Transaction for details.
Action
ALWAYS_BEGIN
_Default
_When it receives a message, Mule always starts a new transaction.BEGIN_OR_JOIN
When it receives a message, Mule joins a transaction if one is already in progress. Otherwise, Mule simply begins a new transaction.
-
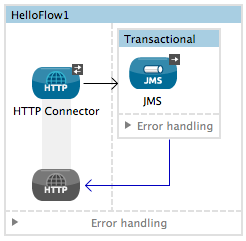
Drag building blocks inside the Transactional scope to build your transaction.
XML Editor
Enterprise
-
To your Mule flow, add one of the following types of
transactionalelements:-
Single Resource transaction
<ee:transactional> </ee:transactional> -
Multiple Resource transaction
<ee:multi-transactional> </ee:multi-transactional> -
XA transaction
<ee:xa-transactional> </ee:xa-transactional>
-
-
Configure two attributes of the transactional element.
Attribute Value Description doc:name
-
Provide a meaningful name for the transaction scope in your flow. Not required in Standalone.
action
ALWAYS_BEGIN
When it receives a message, Mule always starts a new transaction.
BEGIN_OR_JOIN
When it receives a message, Mule joins a transaction if one is already in progress. Otherwise, Mule simply begins a new transaction.
-
Add child elements inside your new transactional scope to build a transaction.
View the Namespace
<mule xmlns:vm="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/vm"
...
xmlns:xsi="
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/vm
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/vm/current/mule-vm.xsd"><flow>
...
<transactional action="BEGIN_OR_JOIN">
<vm:outbound-endpoint path="out1"/>
<vm:outbound-endpoint path="out2"/>
<custom-processor class="org.mule.example.FailingMessageProcessor"/>
<catch-exception-strategy>
<vm:outbound-endpoint path="dead.letter.queue"/>
</catch-exception-strategy>
</transactional>
...
</flow>Configuration Tips and Tricks
-
Operations that occur inside a transaction execute synchronously. You cannot build an asynchronous flow inside a transaction.
-
If you apply an XA transaction to multiple connectors in your flow, be sure to configure the connectors to use XA-enabled resources.
-
If you apply an XA transaction to a JMS inbound connector in your flow, you have the option of specifying the polling frequency of the queue. Access XA Transactions for configuration details.
-
Mule can manage Non-transactional outbound connectors. By default, an outbound connector from a non-transactional transport ignores an active transaction rather than rejecting it. In other words, the default transactional action for such connectors is no longer
NONE. The example code below illustrates this behavior. Mule processes messages it receives from the VM queue synchronously and transactionally. The file transport in the code example is not transactional thus, writing to the file is not part of the transaction. However, if a message throws an exception while Mule is creating the file, Mule rolls back the transaction and reprocesses the message. This example is, in effect, a multiple resource transaction. -
The timeout transaction is only taken into account in XA transactions.
View the Namespace
<mule xmlns:vm="http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/vm"
...
xmlns:xsi="
http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/vm http://www.mulesoft.org/schema/mule/vm/current/mule-vm.xsd"><flow name="transactionalVM">
<vm:inbound-endpoint path="orders" exchange-pattern="one-way">
<vm:transaction action="ALWAYS_BEGIN"/>
</vm:inbound-endpoint>
<file:outbound-endpoint ref="receivedOrders"/>
</flow>Transaction Exception Strategies
To handle exceptions Mule throws while processing transactions, you have three options:
-
Configure no exception strategies for the flow or transaction, thus employing Mule’s default exception strategy.
-
Configure an exception strategy for the flow in which a transaction exists. The flow’s exception strategy handles all exceptions Mule throws while processing the transaction.
-
Configure an exception strategy for the scope of an individual transaction. The transaction’s exception strategy handles all exceptions Mule throws while processing the transaction. If you wish to manage a transactional exception differently from all other exceptions thrown, consider applying an exception strategy to your transaction.
Refer to the Error Handling documentation to learn more about Mule’s default exception strategy and how to apply exception strategies to flows. Follow the steps below to apply an exception strategy to an individual transaction.
Studio Visual Editor
-
Add a Transactional scope to your flow (refer to steps above), then add building blocks within the scope to build a transaction.
-
Search for an exception strategy and drag and drop it into the exception strategy section at the bottom of the scope.
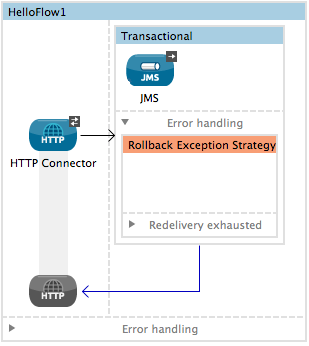
-
Configure the exception strategy as needed, keeping in mind Mule uses this exception strategy to handle any exceptions thrown while processing the transaction. Reference the Error Handling documentation for exception strategy configuration details.
XML Editor
-
Within your
transactionalscope, add anexception-strategychild element at the bottom of the scope.<ee:multi-transactional action="ALWAYS_BEGIN" doc:name="Transactional"> <jdbc-ee:outbound-endpoint exchange-pattern="one-way" queryTimeout="-1" doc:name="Database"/> <rollback-exception-strategy doc:name="Rollback Exception Strategy"/> </ee:multi-transactional> -
Configure the exception strategy as needed, keeping in mind Mule uses this exception strategy to handle any exceptions thrown while processing the transaction. Reference the Error Handling documentation for exception strategy configuration details.
See Also
-
Read more about Single Resource Transactions, Multiple Resource Transactions, and XA Transactions.
-
Read more about Exception Strategies.
-
Consider reading Distributed transactions in Spring, with and without XA, an article on distributed transactions using both XA and non-XA approaches. The multi-resource transaction support described in the example above is related to the Best Efforts 1PC pattern described in the article.
-
Use the Transactions Configuration Reference for quick reference to transactional attributes.



